Ketogenic diet induces an inflammatory reactive astrocytes phenotype reducing glioma growth
- PMID: 39921723
- PMCID: PMC11807044
- DOI: 10.1007/s00018-025-05600-4
Ketogenic diet induces an inflammatory reactive astrocytes phenotype reducing glioma growth
Abstract
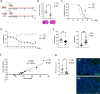
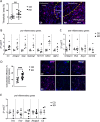
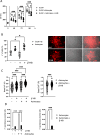
The use of a ketogenic diet (KD) in glioma is currently tested as an adjuvant treatment in standard chemotherapy regimens. The metabolic shift induced by the KD leads to the generation of ketone bodies that can influence glioma cells and the surrounding microenvironment, but the mechanisms have not yet been fully elucidated. Here, we investigated the potential involvement of glial cells as mediators of the KD-induced effects on tumor growth and survival rate in glioma-bearing mice. Specifically, we describe that exposing glioma-bearing mice to a KD or to β-hydroxybutyrate (β-HB), one of the main KD metabolic products, reduced glioma growth in vivo, induced a pro-inflammatory phenotype in astrocytes and increased functional glutamate transporters. Moreover, we described increased intracellular basal Ca2+ levels in GL261 glioma cells treated with β-HB or co-cultured with astrocytes. These data suggest that pro-inflammatory astrocytes triggered by β-HB can be beneficial in counteracting glioma proliferation and neuronal excitotoxicity, thus protecting brain parenchyma.
Keywords: Astrocytes; Astrogliosis; Glioma; Ketogenic diet; Microglia; Pro-inflammatory astrocytes; β-HB.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration. Conflict of interests: All the authors declare no competing interests. Ethical approval: Experiments with mice were approved by the local animal welfare body and by the Italian Ministry of Health (authorization No. 231/2015PR) following the EC Directive 2010/63/EU and the Italian d.lgs.26/2014.
Figures


References
-
- Mukherjee P, Augur ZM, Li M, Hill C, Greenwood B, Domin MA, Kondakci G, Narain NR, Kiebish MA, Bronson RT, Arismendi-Morillo G, Chinopoulos C, Seyfried TN (2019) Therapeutic benefit of combining calorie-restricted ketogenic diet and glutamine targeting in late-stage experimental glioblastoma. Commun Biol 29(2):200. 10.1038/s42003-019-0455-x - PMC - PubMed
-
- Maeyama M, Tanaka K, Nishihara M, Irino Y, Shinohara M, Nagashima H, Tanaka H, Nakamizo S, Hashiguchi M, Fujita Y, Kohta M, Kohmura E, Sasayama T (2021) Metabolic changes and anti-tumor effects of a ketogenic diet combined with anti-angiogenic therapy in a glioblastoma mouse model. Sci Rep 11(1):79 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Maurer GD, Brucker DP, Bähr O, Harter PN, Hattingen E, Walenta S, Mueller-Klieser W, Steinbach JP, Rieger J (2011) Differential utilization of ketone bodies by neurons and glioma cell lines: a rationale for ketogenic diet as experimental glioma therapy. BMC Cancer 26(11):315. 10.1186/1471-2407-11-315 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ciusani E, Vasco C, Rizzo A, Girgenti V, Padelli F, Pellegatta S, Fariselli L, Bruzzone MG, Salmaggi A (2021) MR-spectroscopy and survival in mice with high grade glioma undergoing unrestricted ketogenic diet. Nutr Cancer 73(11–12):2315–2322. 10.1080/01635581.2020.1822423 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

