De novo designed Hsp70 activator dissolves intracellular condensates
- PMID: 39922190
- PMCID: PMC11928274
- DOI: 10.1016/j.chembiol.2025.01.006
De novo designed Hsp70 activator dissolves intracellular condensates
Abstract
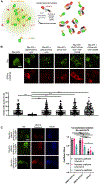
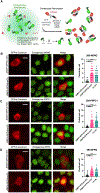
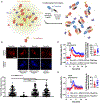
Protein quality control (PQC) is carried out in part by the chaperone Hsp70 in concert with adapters of the J-domain protein (JDP) family. The JDPs, also called Hsp40s, are thought to recruit Hsp70 into complexes with specific client proteins. However, the molecular principles regulating this process are not well understood. We describe the de novo design of Hsp70 binding proteins that either inhibit or stimulate Hsp70 ATPase activity. An ATPase stimulating design promoted the refolding of denatured luciferase in vitro, similar to native JDPs. Targeting of this design to intracellular condensates resulted in their nearly complete dissolution and revealed roles as cell growth promoting signaling hubs. The designs inform our understanding of chaperone structure-function relationships and provide a general and modular way to target PQC systems to regulate condensates and other cellular targets.
Keywords: Hsp70; chaperones; condensates; protein design.
Copyright © 2025 University of Washington. Published by Elsevier Ltd.. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


Update of
-
De novo designed Hsp70 activator dissolves intracellular condensates.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2023 Sep 19:2023.09.18.558356. doi: 10.1101/2023.09.18.558356. bioRxiv. 2023. Update in: Cell Chem Biol. 2025 Mar 20;32(3):463-473.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.chembiol.2025.01.006. PMID: 37781598 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
-
- Hyman AA, Weber CA, and Ju€licher F. (2014). Liquid-Liquid Phase Separation in Biology. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol 30, 39–58. - PubMed
-
- Piette BL, Alerasool N, Lin ZY, Lacoste J, Lam MHY, Qian WW, Tran S, Larsen B, Campos E, Peng J, et al. (2021). Comprehensive interactome profiling of the human Hsp70 network highlights functional differentiation of J domains. Mol. Cell 81, 2549–2565.e8. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

