Bioengineering of a human iPSC-derived vascularized endocrine pancreas for type 1 diabetes
- PMID: 39922198
- PMCID: PMC11866511
- DOI: 10.1016/j.xcrm.2025.101938
Bioengineering of a human iPSC-derived vascularized endocrine pancreas for type 1 diabetes
Abstract
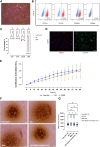
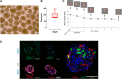
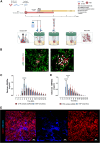
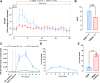
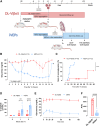
Intrahepatic islet transplantation in patients with type 1 diabetes is limited by donor availability and lack of engraftment. Alternative β cell sources and transplantation sites are needed. We demonstrate the feasibility to repurpose a decellularized lung as an endocrine pancreas for β cell replacement. We bioengineer an induced pluripotent stem cell (iPSC)-based version, fabricating a human iPSC-based vascularized endocrine pancreas (iVEP) using iPSC-derived β cells (iPSC-derived islets [SC-islets]) and endothelial cells (iECs). SC-islets and iECs are aggregated into vascularized iβ spheroids (ViβeSs), and over 7 days of culture, spheroids integrate into the bioengineered vasculature, generating a functional, perfusable human endocrine organ. In vitro, the vascularized extracellular matrix (ECM) sustained SC-islet engraftment and survival with a significantly preserved β cell mass and a physiologic insulin release. In vivo, iVEP restores normoglycemia in diabetic NSG mice. We report a human iVEP providing a controlled in vitro insulin-secreting phenotype and in vivo function.
Keywords: beta cell replacement; extracellular matrix; human iPSC vascularized endocrine spheroids; iPSCs; induced pluripotent stem cells; islet transplantation; lung scaffold; organ decellularization; organ engineering for type 1 diabetes; pancreas bioengineering; tissue engineering; type 1 diabetes.
Copyright © 2025 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- Gregory G.A., Robinson T.I.G., Linklater S.E., Wang F., Colagiuri S., de Beaufort C., Donaghue K.C., International Diabetes Federation Diabetes Atlas Type 1 Diabetes in Adults Special Interest Group. Magliano D.J., Maniam J. Global incidence, prevalence, and mortality of type 1 diabetes in 2021 with projection to 2040: a modelling study. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2022;10:741–760. - PubMed
-
- Beck R.W., Bergenstal R.M., Laffel L.M., Pickup J.C. Advances in technology for management of type 1 diabetes. Lancet. 2019;394:1265–1273. - PubMed
-
- Piemonti L. Felix dies natalis, insulin, ceterum autem censeo ‘beta is better. Acta Diabetol. 2021;58:1287–1306. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

