Carboxymethyl cellulose assisted reforming of poly acrylic acid co methyl methacrylate composite for wastewater treatment and effective hosting of antimicrobial silver
- PMID: 39922883
- PMCID: PMC11807114
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-86214-5
Carboxymethyl cellulose assisted reforming of poly acrylic acid co methyl methacrylate composite for wastewater treatment and effective hosting of antimicrobial silver
Abstract
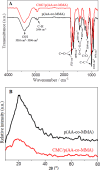
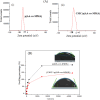
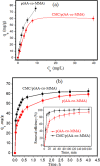
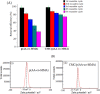
Herein, novel polymer composite is fabricated by hybridizing poly (acrylic acid-co-methyl methacrylate) filaments with carboxymethyl cellulose, which efficiently reorients and strictly ties the fibrous chains to form polymeric units of plate-like morphology. This innovative hybrid polymer composite is analyzed using XRD, FT-IR, swelling and contact angle studies, DLS, AFM, and SEM. Removal efficiency of such polymer composite is scrutinized in colored wastewater treatment. Langmuir and pseudo-first-order kinetic models best describe safranine dye removal from wastewater, adopting exothermic adsorption progression with elevated capacity (~ 59.47 mg/g) and accelerated rate (~ 1.06 h- 1). Such polymer composite exhibits persistent removal efficiency of ~ 90% within 10 min for five consecutive cycles. Hybrid polymer composite is good candidate platform for hosting Ag particles to heighten their antimicrobial activity against Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus, far exceeding 75% reduction. Future studies on applicability of oxygen-rich polymer composites in wastewater treatment and disinfection are optimistic and extremely competent.
Keywords: Adsorption of safranin; Ag particles; Antimicrobial; Carboxymethyl cellulose; Poly (acrylic acid-co-methyl methacrylate).
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Safranin-O cationic dye removal from wastewater using carboxymethyl cellulose-grafted-poly(acrylic acid-co-itaconic acid) nanocomposite hydrogel.Environ Res. 2022 Sep;212(Pt B):113201. doi: 10.1016/j.envres.2022.113201. Epub 2022 Apr 9. Environ Res. 2022. PMID: 35413301
-
Eco-friendly porous carboxymethyl cellulose/dextran sulfate composite beads as reusable and efficient adsorbents of cationic dye methylene blue.Int J Biol Macromol. 2019 Jul 1;132:126-141. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2019.03.164. Epub 2019 Mar 26. Int J Biol Macromol. 2019. PMID: 30926505
-
Free radical synthesis of nanosilver/gelatin-poly (acrylic acid) nanocomposite hydrogels employed for antibacterial activity and removal of Cu(II) metal ions.J Hazard Mater. 2018 Jun 5;351:38-53. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2018.02.017. Epub 2018 Feb 11. J Hazard Mater. 2018. PMID: 29510326
-
Cellulose-g-poly-(acrylamide-co-acrylic acid) polymeric bioadsorbent for the removal of toxic inorganic pollutants from wastewaters.Carbohydr Polym. 2020 Jan 15;228:115396. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2019.115396. Epub 2019 Sep 30. Carbohydr Polym. 2020. PMID: 31635743
-
Novel carboxymethyl cellulose based nanocomposite membrane: Synthesis, characterization and application in water treatment.J Environ Manage. 2016 Jan 15;166:457-65. doi: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2015.10.045. Epub 2015 Nov 10. J Environ Manage. 2016. PMID: 26560638
References
-
- Mekewi, M. A., Madkour, T. M., Darwish, A. S. & Hashish, Y. M. Does poly(acrylic acid-co-acrylamide) hydrogel be the pluperfect choiceness in the treatment of dyeing wastewater? From simple copolymer to gigantic aqua-waste remover. J. Ind. Eng. Chem.30, 359–371 (2015).
-
- Pakdel, P. M., Peighambardoust, S. J., Arsalani, N. & Aghdasinia, H. Safranin-O cationic dye removal from wastewater using carboxymethyl cellulose-grafted-poly(acrylic acid-co-itaconic acid) nanocomposite hydrogel. Environ. Res.212, 113201 (2022). - PubMed
-
- Abdul Hussain, A. F. & Halboos, M. H. Adsorption of safranin dye from their aqueous solutions by using CA and Nano FeO/CA. J. Phys. Conf. Ser.1660, 012080 (2020).
-
- Fayazi, M., Afzali, D., Taher, M. A., Mostafavi, A. & Gupta, V. K. Removal of safranin dye from aqueous solution using magnetic mesoporous clay: Optimization study. J. Mol. Liq.212, 675–685 (2015).
-
- Jabbar, K. Q., Barzinjy, A. A. & Hamad, S. M. Iron oxide nanoparticles: Preparation methods, functions, adsorption and coagulation/flocculation in wastewater treatment. Environ. Nanatechnol. Monit. Manag.17, 100661 (2022).
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

