RBD-displaying OMV nanovaccine boosts immunity against SARS-CoV-2
- PMID: 39923096
- PMCID: PMC11807311
- DOI: 10.1186/s12951-025-03191-7
RBD-displaying OMV nanovaccine boosts immunity against SARS-CoV-2
Abstract
Background: Since the emergence of SARS-CoV-2, the causative agent of COVID-19, the global health landscape has confronted an unprecedented and formidable challenge. The SARS-CoV-2 receptor-binding domain (RBD) is a key antigen in vaccine design. However, its low immunogenicity has been a hurdle, resulting in the production of minimal anti-RBD antibodies even when combined with alum adjuvant. Outer membrane vesicles (OMVs), secreted by Gram-negative bacteria, are nanospherical structures that can display or deliver antigens while also providing adjuvant activity through pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs).
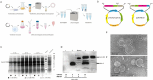
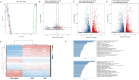
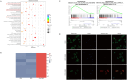
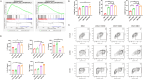
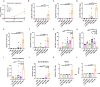
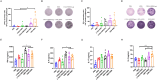
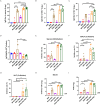
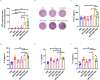
Results: In this study, we utilized the SpyTag (ST)/SpyCatcher (SC) bioconjugation system to couple OMV and SARS-CoV-2 RBD in vitro. We successfully prepared a 'plug-and-display' nanovaccine OMV-RBD, which demonstrated good safety profiles and promoted the uptake of antigens by DCs and the maturation of BMDCs by activating TLR3 and NOD2 signaling pathways. Both intranasal and intramuscular immunization with OMV-RBD vaccine elicited robust antigen-specific humoral and cellular immune responses. Importantly, the induced antibodies effectively inhibited the binding of RBD to human angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (hACE2) and neutralized SARS-CoV-2 pseudoviruses.
Conclusions: This vaccine platform offers an alternative strategy for developing recombinant subunit vaccines against SARS-CoV-2, potentially enhancing immune responses and improving vaccine efficacy.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: The Animal Ethics Committee of Army Medical University has approved all animal experiments. Trained experimentalists adhered to the 3R principle at all times during the experiment to avoid unnecessary suffering of the animals. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Le Thanh T, Andreadakis Z, Kumar A, Gomez Roman R, Tollefsen S, Saville M, et al. The COVID-19 vaccine development landscape. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2020;19(5):305–6. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

