Sustainable Ultrasound-Assisted Solid-Phase peptide synthesis (SUS-SPPS): Less Waste, more efficiency
- PMID: 39923348
- PMCID: PMC11849595
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ultsonch.2025.107257
Sustainable Ultrasound-Assisted Solid-Phase peptide synthesis (SUS-SPPS): Less Waste, more efficiency
Abstract
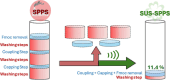
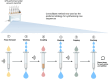
The integration of low-frequency ultrasound with Solid-Phase Peptide Synthesis (SPPS) was explored to establish a Sustainable Ultrasound-assisted Solid-Phase Peptide Synthesis (SUS-SPPS) method. This innovative approach significantly reduces solvent consumption, washing steps, time, and reagent usage compared to conventional manual SPPS protocols. The SUS-SPPS method exploits ultrasound at every stage of synthesis and work-up, reducing the process to just two steps. The first step sequentially combines Fmoc-amino acid coupling, capping of unreacted amino groups, and Fmoc deprotection into a single operation, while the second one consists of a single washing procedure. Moreover, we demonstrated that the method is compatible with various resin types, including Rink-amide, Wang, and Cl-Trt resins, and facilitates the efficient synthesis of peptides of varying lengths (up to 20-mers) and compositions, including those traditionally considered "difficult sequences", with excellent yields and purity. Notably, SUS-SPPS reduces solvent usage per coupling cycle by 83-88%, marking a significant breakthrough in sustainable peptide synthesis.
Keywords: Green approach; Minimized solvent consumption; Solid-Phase Synthesis; Sonochemistry; Sustainable Peptide Synthesis; Ultrasound.
Copyright © 2025 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of competing interest The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures









References
-
- P.T. Anastas and J.C. Warner, Green chemistry: Theory and practice, ed. Oxford University Press, Oxford, 2000. https://doi.org/10.1093/oso/9780198506980.001.0001.
-
- Erythropel H.C., Zimmerman J.B., de Winter T.M., Petitjean L., Melnikov F., Lam C.H., Lounsbury A.W., Mellor K.E., Janković N.Z., Tu Q., Pincus L.N., Falinski M.M., Shi W., Coish P., Plata D.L., Anastas P.T. The Green ChemisTREE: 20 years after taking root with the 12 principles. Green Chem. 2018;20:1929–1961. doi: 10.1039/C8GC00482J. - DOI
-
- Alder C.M., Hayler J.D., Henderson R.K., Redman A.M., Shukla L., Shuster L.E., Sneddon H.F. Updating and further expanding GSK's solvent sustainability guide. Green Chem. 2016;18:3879–3890. doi: 10.1039/C6GC00611F. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

