Real-world outcomes with tisagenlecleucel in aggressive B-cell lymphoma: subgroup analyses from the CIBMTR registry
- PMID: 39924174
- PMCID: PMC11808862
- DOI: 10.1136/jitc-2024-009890
Real-world outcomes with tisagenlecleucel in aggressive B-cell lymphoma: subgroup analyses from the CIBMTR registry
Abstract
Background: Tisagenlecleucel, a CD19 chimeric antigen receptor T-cell therapy, is approved for adults with relapsed or refractory (R/R) diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) or high-grade B-cell lymphoma (HGBCL) after ≥2 lines of therapy. When used in real-world settings, tisagenlecleucel has shown similar efficacy and improved safety compared with previous clinical trials. However, long-term data on real-world outcomes are lacking.
Methods: Clinical data from a cohort of patients treated with tisagenlecleucel in a real-world setting were captured in the Center for International Blood and Marrow Transplant Research registry. The main clinical outcomes analysed included response rate, duration of response, survival, adverse events and clinicopathologic and treatment characteristics that may affect those outcomes.
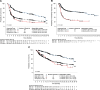
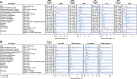
Results: As of May 2022, 1159 patients with R/R DLBCL/HGBCL received tisagenlecleucel. The overall response rate was 59.5%, and the complete response rate was 44.5%. With a median follow-up of 23.2 months in the efficacy set (n=968), the 24 month rates of progression-free survival, ongoing response and overall survival were 28.4%, 52.6% and 43.6%, respectively. Grade ≥3 cytokine release syndrome and neurotoxicity were reported in 6% and 7.4% of patients, respectively. Patients with DLBCL (vs HGBCL), complete response before infusion, prior autologous or allogeneic haematopoietic stem cell transplant and lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) within normal limits experienced more favourable efficacy outcomes, and those with Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group performance status of ≥2, ≥3 prior lines of therapy, elevated LDH and fludarabine-based lymphodepleting chemotherapy experienced less favourable safety outcomes.
Conclusions: This real-world study of tisagenlecleucel for patients with R/R DLBCL/HGBCL shows consistent efficacy and better safety outcomes than the pivotal trial. This study also identifies baseline disease characteristics and prior or concurrent treatments that may affect clinical outcomes.Tisagenlecleucel, a CD19 chimeric antigen receptor T-cell therapy, is approved for adults with relapsed or refractory (R/R) diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) or high-grade B-cell lymphoma (HGBCL) after ≥2 lines of therapy. When used in real-world settings, tisagenlecleucel has shown similar efficacy and improved safety compared with previous clinical trials. However, long-term data on real-world outcomes are lacking.Clinical data from a cohort of patients treated with tisagenlecleucel in a real-world setting were captured in the Center for International Blood and Marrow Transplant Research registry. The main clinical outcomes analysed included response rate, duration of response, survival, adverse events, and clinicopathologic and treatment characteristics that may affect those outcomes.As of May 2022, 1159 patients with R/R DLBCL/HGBCL received tisagenlecleucel. The overall response rate was 59.5%, and the complete response rate was 44.5%. With a median follow-up of 23.2 months in the efficacy set (n=968), the 24 month rates of progression-free survival, ongoing response, and overall survival were 28.4%, 52.6%, and 43.6%, respectively. Grade ≥3 cytokine release syndrome and neurotoxicity were reported in 6% and 7.4% of patients, respectively. Patients with DLBCL (vs HGBCL), complete response before infusion, prior autologous or allogeneic haematopoietic stem cell transplant, and lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) within normal limits experienced more favourable efficacy outcomes, and those with Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group performance status ≥2, ≥3 prior lines of therapy, elevated LDH, and fludarabine-based lymphodepleting chemotherapy experienced less favourable safety outcomes.In conclusion, this real-world study of tisagenlecleucel for patients with R/R DLBCL/HGBCL shows consistent efficacy and better safety outcomes than the pivotal trial. This study also identifies baseline disease characteristics and prior or concurrent treatments that may affect clinical outcomes.
Keywords: B cell; Chimeric antigen receptor - CAR; Hematologic Malignancies; Immunotherapy; Lymphoma.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2025. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ Group.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: DJL: ADC Therapeutics, Calithera, Epizyme, Karyopharm, Morphosys: Membership on an entity’s Board of Directors or advisory committees; Curis, Triphase: Research funding. MJF: BMS, JnJ/Legend, Iovance, Novartis, Kite/Gilead, Cytoagents: Consultancy; Novartis, Kite/Gilead, Arcellx: Research funding. MH: none. SRF: Novartis, Janssen, BMS: consultancy, honoraria and Speakers bureau. BTH: Kite/Gilead: Membership on an entity’s Board of Directors or advisory committees, travel support; Kite/Gilead, Novartis, BMS: Consultancy, honoraria, and research funding. GS: None. CAJ: Kite/Gilead, Pfizer: Research funding; Kite/Gilead, Novartis, BMS/Celgene, Lonza, Ispen, Epizyme, Bluebird Bio, Instil Bio, ImmPACT Bio, Daiichi Sankyo, AbbVie, Humanigen, Nkarta, Precision BioSciences: Consultancy and honoraria; Axis, Clinical Care Options: Speakers bureau; Novartis, Lonza, Humanigen, Precision BioSciences: Travel support. SJ: Kite, Novartis: Research funding; CRISPR Therapeutics, Kite, Novartis, Gamida: Consultancy. FLL: Allogene, Bluebird Bio, Kite/Gilead, Novartis, BMS, CERo Therapeutics, National Cancer Institute, Leukemia and Lymphoma Society: Research funding; Allogene, Amgen, Bluebird Bio, BMS/Celgene, Cellular Biomedicine Group, Calibr, Cowen, EcoR1, Emerging Therapy Solutions, Gerson Lehrman Group, GammaDelta Therapeutics, Iovance, Janssen, Kite/Gilead, Legend Biotech, Novartis, Umoja, Wugen, Celgene, A2, Daiichi Sankyo, Sana, Takeda: Consultancy; Aptitude Health, ASH, BioPharm Communications, CAREducation, Clinical Care Options Oncology, Imedex, Society for Immunotherapy of Cancer: Education or editorial activity; Other: patents, royalties, other intellectual property from several patents held by the institution in my name (unlicensed) in the field of cellular immunotherapy. RR: Gilead, Novartis, Takeda, BMS: Honoraria. PAR: BMS, ADC Therapeutics, Kite/Gilead, Novartis, Nektar Therapeutics, Intellia Therapeutics, BeiGene, Janssen, Pharmacyclics, CVS Caremark, Genmab, AbbVie: Membership on an entity’s Board of Directors or advisory committees; BMS, Kite/Gilead, Novartis, CRISPR Therapeutics, MorphoSys, Calibr, Tessa Therapeutics, Fate Therapeutics, Xencor, Genentech: Research funding; BMS, Kite/Gilead, Novartis, Sana Biotechnology, BeiGene: Consultancy; Novartis: Honoraria; Kite/Gilead: Speakers bureau. GLS: Janssen, Amgen, Beyond Spring, BMS: Research Funding. LLP: none. RT: Novartis, current employment. SL: Novartis, current employment. MM: Novartis, current employment. AM: Novartis, current employment and current holder of stock options in a privately held company. MCP and BMS, Novartis, Kite, Janssen, Research funding; BMS: consultancy. CJT: Nektar Therapeutics, Caribou Biosciences, T-CURX, Myeloid Therapeutics, Arsenal Bio, Century Therapeutics, Cargo Therapeutics, eGlint, Differentia Bio, Advesya, IGM Therapeutics, GSK, Decheng Capital, Boxer Capital, Kite/Gilead, Novartis, Allogene, Legend Bio, Kyverna, Expert Connect, Prescient Therapeutics, AbbVie: Consultancy and advisory roles; Juno Therapeutics, Nektar Therapeutics, Nanostring: Research funding; Fred Hutchinson Cancer Center: Patents and royalties; Caribou Bioscience, Myeloid Therapeutics, Arsenal Bio, eGlint Cargo Therapeutics: Current holder of stock options in a privately held company.
Figures
References
-
- Schuster SJ, Tam CS, Borchmann P, et al. Long-term clinical outcomes of tisagenlecleucel in patients with relapsed or refractory aggressive B-cell lymphomas (JULIET): a multicentre, open-label, single-arm, phase 2 study. Lancet Oncol. 2021;22:1403–15. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(21)00375-2. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 AI158861/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA231838/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI126612/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U24 HL157560/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL155741/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL128568/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA008748/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- OT3 HL147741/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA100019/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI150999/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P01 CA111412/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA218285/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA152108/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI128775/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U24 CA076518/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U24 HL138660/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI069197/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA231141/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 CA121947/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U24 CA233032/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA262899/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL131731/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
