Evaluating Activated Regulatory T Cells as a Biomarker of Chronic Allograft Inflammation in Pediatric Kidney Transplant Recipients
- PMID: 39924341
- PMCID: PMC11807789
- DOI: 10.1111/petr.70041
Evaluating Activated Regulatory T Cells as a Biomarker of Chronic Allograft Inflammation in Pediatric Kidney Transplant Recipients
Abstract
Background: There is a need for noninvasive immunological biomarkers that can identify stable kidney allograft immune quiescence to inform individualized immunosuppression.
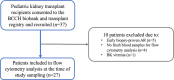
Methods: We conducted a cross-sectional, pilot cohort study evaluating the relative abundance of regulatory T cells (Tregs) to effector T-cell (Teff) populations as a surrogate marker of long-term graft tolerance. We obtained fresh peripheral blood mononuclear cell samples from stable pediatric kidney transplant recipients, most with recent surveillance biopsies to identify the presence or absence of chronic inflammation. Tregs were sub-phenotyped as naïve, memory, and activated Tregs (aTreg). Treg/Teff ratios were modeled for association with chronic inflammation and in the context of potential clinical features.
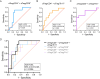
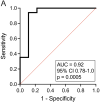
Results: Twenty-seven patient samples were included on standard immunosuppression (tacrolimus, mycophenolate, and prednisone) with a mean age of 9.2 ± 5.0 years, at 30.2 ± 21.7 months posttransplant. The ratio of aTreg (FOXP3++CD45RA-) to Th17 cells (CD4+IL-17+) was significantly greater in patients without inflammation than in patients with graft inflammation (p < 0.01). Similarly, there was a trend toward greater aTreg/CD4+ T cells and aTreg/CD8+ Teff in patients without inflammation (p = 0.05 and 0.09, respectively). There was no significant association for inflammation with naïve or memory Treg/Teff ratios. Multiple logistic regression with all three aTreg/Teff ratios modeled allograft inflammation with high sensitivity and specificity (AUC = 0.83, 95% CI 0.67-0.98).
Conclusions: The proportion of peripheral blood aTregs/Teff cells in this pilot cohort of stable pediatric kidney transplant recipients was associated with immune quiescence. These data support further investigation into aTreg/Teff monitoring to inform precision immunosuppressive treatment.
Keywords: Treg/Teff; immune biomarkers; kidney transplantation; regulatory T cells.
© 2025 The Author(s). Pediatric Transplantation published by Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

