The Mechanisms of Sepsis Induced Coagulation Dysfunction and Its Treatment
- PMID: 39925935
- PMCID: PMC11804232
- DOI: 10.2147/JIR.S504184
The Mechanisms of Sepsis Induced Coagulation Dysfunction and Its Treatment
Abstract
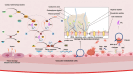
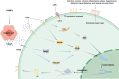
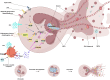
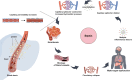
Sepsis is a critical condition characterized by organ dysfunction due to a dysregulated response to infection that poses significant global health challenges. Coagulation dysfunction is nearly ubiquitous among sepsis patients. Its mechanisms involve platelet activation, coagulation cascade activation, inflammatory reaction imbalances, immune dysregulation, mitochondrial damage, neuroendocrine network disruptions, and endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress. These factors not only interact but also exacerbate one another, leading to severe organ dysfunction. This review illustrates the mechanisms of sepsis-induced coagulopathy, with a focus on tissue factor activation, endothelial glycocalyx damage, and the release of neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs), all of which are potential targets for therapeutic interventions.
Keywords: coagulation dysfunction; sepsis; thrombosis.
© 2025 Zhu et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

