State of the ART: Drug Screening Reveals Artesunate as a Promising Anti-Fibrosis Therapy
- PMID: 39925974
- PMCID: PMC11800322
- DOI: 10.70322/jrbtm.2024.10023
State of the ART: Drug Screening Reveals Artesunate as a Promising Anti-Fibrosis Therapy
Abstract
Fibrosis is a progressive pathological process that severely impairs normal organ function. Current treatments for fibrosis are extremely limited, with no curative approaches available. In a recent article published in Cell, Zhang and colleagues employed drug screening using ACTA2 reporter iPSC-derived cardiac fibroblasts and identified artesunate as a potent antifibrotic drug by targeting MD2/TLR4 signaling. This study provides new insights into strategies for exploiting existing drugs to treat fibrosis.
Keywords: Artesunate; Drug screening; Fibrosis; MD2/TLR4.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Competing Interest The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships.
Figures
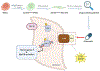
Comment on
-
Multiscale drug screening for cardiac fibrosis identifies MD2 as a therapeutic target.Cell. 2024 Dec 12;187(25):7143-7163.e22. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2024.09.034. Epub 2024 Oct 15. Cell. 2024. PMID: 39413786
References
-
- Rockey DC, Bell PD, Hill JA. Fibrosis—a common pathway to organ injury and failure. N. Engl. J. Med 2015, 372, 1138–1149. - PubMed
-
- King TE Jr., Bradford WZ, Castro-Bernardini S, Fagan EA, Glaspole I, Glassberg MK, et al. A phase 3 trial of pirfenidone in patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. N. Engl. J. Med 2014, 370, 2083–2092. - PubMed
-
- Richeldi L, du Bois RM, Raghu G, Azuma A, Brown KK, Costabel U, et al. Efficacy and safety of nintedanib in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. N. Engl. J. Med 2014, 370, 2071–2082. - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
