Crosstalk of SPINK4 Expression With Patient Mortality, Immunotherapy and Metastasis in Pan-Cancer Based on Integrated Multi-Omics Analyses
- PMID: 39926372
- PMCID: PMC11806753
- DOI: 10.2147/OTT.S487126
Crosstalk of SPINK4 Expression With Patient Mortality, Immunotherapy and Metastasis in Pan-Cancer Based on Integrated Multi-Omics Analyses
Abstract
Background: Cancer remains a major global health challenge, with early detection and prompt treatment being crucial for reducing mortality rates. The SPINK4 has been linked to the development of several tumors, and there is growing evidence of its involvement. However, its specific functions and effects in different cancer types remain unclear.
Methods: The association between SPINK4 expression levels and tumor progression was investigated and confirmed using the TCGA dataset. Kaplan-Meier curves were utilized to examine the correlation between SPINK4 expression with survival outcomes in pan-cancer patients. The Pearson method was employed to investigate the association of SPINK4 expression with the tumor microenvironment, stemness score, immunoinfiltrating subtype, and chemotherapy sensitivity in human different cancer types. Wound healing and Transwell assays were performed to confirm the roles of the model gene in colon adenocarcinoma cells.
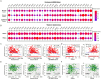
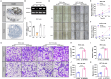
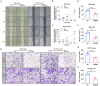
Results: The expression of SPINK4 shows heterogeneity across pan-cancer tissues, and is closely associated with poor prognosis, immune cell invasion, tumor cell resistance, and tumor metastasis in a various human cancer. Mutation of SPINK4 hold significant predictive value for poor prognosis of pan-cancer patients. In addition, SPINK4 expression was significantly correlated with the tumor microenvironment (stromal cells and immune cells) and stemness score (DNAss and RNAss) in human pan-cancer tissues, particularly in BLCA and COAD. Single-cell sequencing analysis showed that SPINK4 is mainly expressed in endothelial cells in BLCA and in malignant cells in COAD. Drug resistance analysis showed a significant association between SPINK4 expression and sensitivity to several cancer chemotherapy drugs. Importantly, overexpression of SPINK4 promoted the metastasis of colon cancer cell lines (HCT116 and RKO), whereas SPINK4 knockout markedly inhibited their metastasis.
Conclusion: These findings reveal the crucial role of SPINK4 in the pan-cancer process and may have significant implications for the diagnosis and treatment of cancer in the future.
Keywords: drug sensitivity; genetic alteration; immune infiltration; pan-cancer analysis; single-cell sequencing.
© 2025 Cao et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests in this work.
Figures





References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

