Frequency of trigeminal neurovascular contacts identified on 3D-fast imaging employing steady-state acquisition magnetic resonance imaging in asymptomatic adults
- PMID: 39926468
- PMCID: PMC11799694
- DOI: 10.25259/SNI_1021_2024
Frequency of trigeminal neurovascular contacts identified on 3D-fast imaging employing steady-state acquisition magnetic resonance imaging in asymptomatic adults
Abstract
Background: Neurovascular conflict is considered one of the main causes of Trigeminal neuralgia, and 3D fast imaging employing steady-state acquisition magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is the diagnostic imaging of choice. However, no tool is available to confirm imaging findings as the primary cause of trigeminal neuralgia because neurovascular contact is frequently found in asymptomatic individuals, according to some literature, although very little data is available till now. Therefore, we aim to determine the frequency of trigeminal neurovascular contact, involved nerve segment, culprit vessel, and characteristics of contacts in asymptomatic individuals. Knowledge about this is very crucial so that every patient may not be labeled as having neurovascular conflict as the primary cause and can be saved from unnecessary surgeries.
Methods: A retrospective observational study was conducted on 105 MRI brain scans of asymptomatic individuals for trigeminal neurovascular relationships by two expert neuro-radiologists. Percentages calculated for categorical variables and for continuous variables Shapiro-Wilk test were used. The Fisher Exact test is used to assess the association between conflict and other variables. Inter-rater reliability was computed for the outcome and other variables and Cohen's kappa to evaluate the strength of agreement. All calculations were performed using STATA version 17.0.
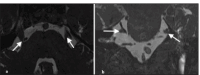
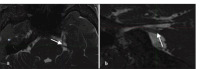
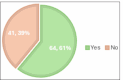
Results: Out of 105 cases, neuro-vascular contact was identified in 64 cases. The most common contacting vessel was the superior cerebellar artery. The most common nerve segment involved was the cisternal segment, followed by the Root entry zone and porous trigeminus. In about 54 cases, the vessel was abutting the nerve, while in eight cases, it was compressing and, in two cases, displacing the nerve. The superior surface of the nerve was commonly involved. The inter-rater reliability between both neuroradiologists showed significant agreement.
Conclusion: Neurovascular contact is found in asymptomatic individuals, so just the presence of contact in symptomatic individuals on MRI should not be considered as only the cause of trigeminal neuralgia. It is important to identify nerve thinning and distortion, which are more reliable signs.
Keywords: 3D-constructive interference in steady state; 3D-fast imaging employing steady-state acquisition magnetic resonance imaging; Magnetic resonance image; Neurovascular conflict; Trigeminal neuralgia.
Copyright: © 2025 Surgical Neurology International.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Ahmad HS, Blue R, Ajmera S, Heman-Ackah S, Spadola M, Lazor JW, et al. The influence of radiologist practice setting on identification of vascular compression from magnetic resonance imaging in trigeminal neuralgia. World Neurosurg. 2023;171:e398–403. - PubMed
-
- Anwar HA, Ramya Krishna M, Sadiq S, Ramesh Kumar R, Venkatarathnam V, Saikiran G. A study to evaluate neurovascular conflict of trigeminal nerve in trigeminal neuralgia patients with the help of 1.5 T MR imaging. Egypt J Radiol Nucl Med. 2022;53:66.
-
- Cavusoglu M, Cılız DS, Duran S, Ozsoy A, Elverici E, Karaoglanoglu R, et al. Temporal bone MRI with 3D-FIESTA in the evaluation of facial and audiovestibular dysfunction. Diagn Interv Imaging. 2016;97:863–9. - PubMed
-
- Darrow DP, Mulford KL, Quinn C, Spano A, Nixdorf DR, Grande A, et al. The practical limits of high-quality magnetic resonance imaging for the diagnosis and classification of trigeminal neuralgia. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2022;221:107403. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
