Dispersal dynamics and introduction patterns of SARS-CoV-2 lineages in Iran
- PMID: 39926479
- PMCID: PMC11803630
- DOI: 10.1093/ve/veaf004
Dispersal dynamics and introduction patterns of SARS-CoV-2 lineages in Iran
Abstract
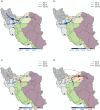
Understanding the dispersal patterns of Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus-2 (SARS-CoV-2) lineages is crucial to public health decision-making, especially in countries with limited access to viral genomic sequencing. This study provides a comprehensive epidemiological and phylodynamic perspective on SARS-CoV-2 lineage dispersal in Iran from February 2020 to July 2022. We explored the genomic epidemiology of SARS-CoV-2 combining 1281 genome sequences with spatial data in a phylogeographic framework. Our analyses shed light on multiple international imports seeding subsequent waves and on domestic dispersal dynamics. Lineage B.4 was identified to have been circulating in Iran, 29 days (95% highest probability density interval: 21-47) before non-pharmaceutical interventions were implemented. The importation dynamics throughout subsequent waves were primarily driven from the country or region where the variant was first reported and gradually shifted to other regions. At the national level, Tehran was the main source of dissemination across the country. Our study highlights the crucial role of continuous genomic surveillance and international collaboration for future pandemic preparedness and efforts to control viral transmission.
Keywords: COVID-19; Iran; SARS-CoV-2; dispersal dynamic; epidemic; genomic epidemiology; pandemic; phylogenetic; preparedness; surveillance; transmission; travel; variants; vigilance.
© The Author(s) 2025. Published by Oxford University Press.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Aksamentov I, Roemer C, Hodcroft E et al. Nextclade: clade assignment, mutation calling and quality control for viral genomes. J Open Source Softw 2021;6:3773.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

