Evaluation of the Gly-Phe-Lys Linker to Reduce the Renal Radioactivity of a [64Cu]Cu-Labeled Multimeric cRGD Peptide
- PMID: 39926504
- PMCID: PMC11799997
- DOI: 10.1021/acsomega.4c10621
Evaluation of the Gly-Phe-Lys Linker to Reduce the Renal Radioactivity of a [64Cu]Cu-Labeled Multimeric cRGD Peptide
Abstract
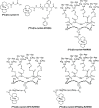
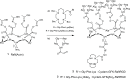
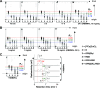
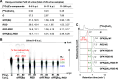
Radiometal-labeled peptide-based radiopharmaceuticals (RLPB-radiopharmaceuticals) are promising for cancer imaging and targeted radiotherapy; however, their effectiveness is often compromised by the high retention of nonspecific radioactivity in the kidneys due to renal excretion pathways. Current strategies to address this issue have limitations, highlighting the need for innovative approaches to improve targeting specificity and therapeutic efficacy. We aimed to evaluate the applicability of the Gly-Phe-Lys (GFK) tripeptide, a renal brush border (RBB) enzyme-cleavable linkage, to reduce renal radioactivity in RLPB-radiopharmaceuticals using the integrin-targeting radiopeptide [64Cu]Cu-cyclam-RAFT-c(-RGDfK-)4 ([64Cu]Cu-cyclam-RaftRGD). We designed and synthesized the model compound [64Cu]Cu-cyclam-GFK(benzoyl [Bz]), its predictive metabolites, and GFK-incorporated [64Cu]Cu-cyclam-RaftRGD derivatives [64Cu]Cu-cyclam-GFK-RaftRGD and [64Cu]Cu-cyclam-GFK(beta-alanine [βA])3-RaftRGD. In vitro studies showed that dual radiometabolites, namely, [64Cu]Cu-cyclam-G and [64Cu]Cu-cyclam-GF, were simultaneously released from [64Cu]Cu-cyclam-GFK(Bz) by different RBB enzymes, whereas both RaftRGD derivatives released only [64Cu]Cu-cyclam-GF. When injected into mice, [64Cu]Cu-cyclam-GFK(Bz) and the two RaftRGD derivatives led to the urinary excretion of [64Cu]Cu-cyclam-G and [64Cu]Cu-cyclam-GF, respectively. PET imaging and biodistribution studies showed the increased rates of reduction in renal radioactivity levels for the two RaftRGD derivatives compared to the parental [64Cu]Cu-cyclam-RaftRGD (e.g., PET: 1 to 24 h postinjection, 73.0 ± 2.3 and 75.6 ± 1.8 vs 43.0 ± 4.5%, p < 0.0001; biodistribution: 3 to 24 h, 61.1 and 74.4 vs 22.8%). Taken together, these results indicate that the designed renal cleavage occurred in vivo. We also noted the steric interference of the RaftRGD moiety on enzyme access, the spacer effect of the trimeric βA sequence (reduced steric hindrance), and the altered radiopharmacokinetics (e.g., initially increased renal accumulation) of the RaftRGD compounds upon linker incorporation. These findings provide important insights into the chemical design of RLPB-radiopharmaceuticals with reduced renal retention based on the RBB strategy.
© 2025 The Authors. Published by American Chemical Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures







Similar articles
-
Uniform intratumoral distribution of radioactivity produced using two different radioagents, 64Cu-cyclam-RAFT-c(-RGDfK-)4 and 64Cu-ATSM, improves therapeutic efficacy in a small animal tumor model.EJNMMI Res. 2018 Jun 19;8(1):54. doi: 10.1186/s13550-018-0407-3. EJNMMI Res. 2018. PMID: 29923139 Free PMC article.
-
PET imaging and biodistribution analysis of the effects of succinylated gelatin combined with L-lysine on renal uptake and retention of ⁶⁴Cu-cyclam-RAFT-c(-RGDfK-)₄ in vivo.Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2014 Apr;86(3):478-86. doi: 10.1016/j.ejpb.2013.11.006. Epub 2013 Dec 4. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2014. PMID: 24316338
-
Radiotheranostic Agent 64Cu-cyclam-RAFT-c(-RGDfK-)4 for Management of Peritoneal Metastasis in Ovarian Cancer.Clin Cancer Res. 2020 Dec 1;26(23):6230-6241. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-20-1205. Epub 2020 Sep 15. Clin Cancer Res. 2020. PMID: 32933998
-
Strategies to reduce renal radioactivity levels of antibody fragments.Q J Nucl Med. 1998 Dec;42(4):262-70. Q J Nucl Med. 1998. PMID: 9973841 Review.
-
[Design of radiolabeled antibody fragments for tumor-selective radioactivity localization--brush border enzyme-sensitive bond to decrease renal accumulation of radioactivity].Yakugaku Zasshi. 2003 Aug;123(8):647-52. doi: 10.1248/yakushi.123.647. Yakugaku Zasshi. 2003. PMID: 12931660 Review. Japanese.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
