Assessment of the Antibacterial Properties and Cytocompatibility of Implant Coatings Incorporating Antimicrobial Agents: An In vitro Study
- PMID: 39927006
- PMCID: PMC11805164
- DOI: 10.4103/jpbs.jpbs_1104_24
Assessment of the Antibacterial Properties and Cytocompatibility of Implant Coatings Incorporating Antimicrobial Agents: An In vitro Study
Abstract
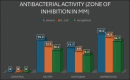
Objective: This study evaluates the antibacterial efficacy and cytocompatibility of titanium implants coated with silver, chitosan, and antibiotics.
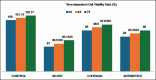
Materials and methods: Antibacterial properties were tested using inhibition zones against S. aureus, E. coli, and P. aeruginosa. The cytocompatibility was assessed through cell viability, adhesion, and proliferation by using human osteoblast-like cells (MG-63). Statistical analysis was performed using ANOVA and Tukey's HSD test.
Results: Antibiotics showed the highest antibacterial activity. Silver reduced cell viability, adhesion, and proliferation, while chitosan balanced antibacterial efficacy and biocompatibility. Time-dependent viability assays indicated consistent reduction for silver-treated cells.
Conclusion: Silver, chitosan, and antibiotics are effective against implant-related pathogens, but their cytocompatibility varies.
Keywords: Antibacterial efficacy; antibiotics; antimicrobial coatings; dental implants.
Copyright: © 2024 Journal of Pharmacy and Bioallied Sciences.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Alghamdi HS, Jansen JA. The development and future of dental implants. Dent Mater J. 2020;39:167–72. - PubMed
-
- Zhang J, Gao M, Gao W, Yang P, Meng F, Liu Q, et al. Functional Silver nanoparticles as broad-spectrum antimicrobial agents. N J Chem. 2022;46:16387–93.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources