Circulating levels of miR-20b-5p are associated with survival in cardiogenic shock
- PMID: 39927096
- PMCID: PMC11804825
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jmccpl.2025.100284
Circulating levels of miR-20b-5p are associated with survival in cardiogenic shock
Abstract
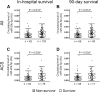
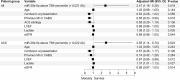
Cardiogenic shock (CS) is a medical emergency with high in-hospital mortality. New biomarkers are needed to identify patients at a greater risk of adverse outcomes. This study aimed to investigate the prognostic potential of microRNAs (miRNAs) in assessment of the outcome of cardiogenic shock. Circulating miRNA levels were measured by quantitative PCR in plasma samples collected at baseline from 165 patients of the multicenter, prospective, observational CardShock study and compared between in-hospital and 90-day survivors and non-survivors. Of the 10 studied miRNAs, median levels of miR-20b-5p at baseline were significantly higher in in-hospital and 90-day survivors compared to non-survivors [median 0.014 arbitrary units (AU) (interquartile range (IQR) 0.003-0.024) vs. 0.008 AU (IQR 0.001-0.015), p = 0.013] and [0.015 AU (IQR 0.003-0.025) vs. 0.010 AU (IQR 0.001-0.015), p = 0.012], respectively. In Cox regression analysis, miR-20b-5p levels in the highest quartile were significantly associated with 90-day survival (adjusted hazard ratio 2.47 (95 % confidence interval 1.16-5.28), p = 0.019) when adjusted for CardShock Risk Score variables (age, confusion at presentation, previous myocardial infarction or coronary artery bypass grafting, acute coronary syndrome (ACS) etiology, left ventricular ejection fraction, lactate, and estimated glomerular filtration rate). A similar association of highest quartile miR-20b-5p levels with 90-day survival was also confirmed in ACS patient subcohort (79 % of CS patients). The results of this study indicate that circulating levels of miR-20b-5p at baseline could help in assessing in-hospital and 90-day survival in CS patients.
Keywords: Biomarker; Cardiogenic shock; Survival; miR-20b-5p; microRNA.
© 2025 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
Yvan Devaux holds patents on RNA biomarkers of cardiovascular disease, is a member of the Scientific Advisory Board of Firalis SA, and is a member of the Editorial Board of The Journal of Molecular and Cellular Cardiology Plus. The other authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Palacios Ordonez C., Garan A.R. The landscape of cardiogenic shock: epidemiology and current definitions. Curr Opin Cardiol. 2022;37:236–240. - PubMed
-
- van Diepen S., Katz J.N., Albert N.M., Henry T.D., Jacobs A.K., Kapur N.K., et al. Contemporary management of cardiogenic shock: a scientific statement from the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2017;136 e232-e68. - PubMed
-
- Kapur N.K., Kanwar M., Sinha S.S., Thayer K.L., Garan A.R., Hernandez-Montfort J., et al. Criteria for defining stages of cardiogenic shock severity. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2022;80:185–198. - PubMed
-
- Baran D.A., Grines C.L., Bailey S., Burkhoff D., Hall S.A., Henry T.D., et al. SCAI clinical expert consensus statement on the classification of cardiogenic shock: this document was endorsed by the American College of Cardiology (ACC), the American Heart Association (AHA), the Society of Critical Care Medicine (SCCM), and the Society of Thoracic Surgeons (STS) in April 2019. Catheter Cardiovasc Interv. 2019;94:29–37. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

