Immunogenicity and protective efficacy of a multi-antigenic adenovirus-based vaccine candidate against Mycobacterium tuberculosis
- PMID: 39927262
- PMCID: PMC11802578
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2025.1492268
Immunogenicity and protective efficacy of a multi-antigenic adenovirus-based vaccine candidate against Mycobacterium tuberculosis
Erratum in
-
Erratum: Immunogenicity and protective efficacy of a multi-antigenic adenovirus-based vaccine candidate against Mycobacterium tuberculosis.Front Microbiol. 2025 May 22;16:1605861. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2025.1605861. eCollection 2025. Front Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 40475384 Free PMC article.
Abstract
Introduction: The inadequate efficacy of the Bacillus Calmette-Guérin (BCG) vaccine against adult pulmonary tuberculosis (TB) necessitates the development of new and effective vaccines. Human adenovirus serotype 5 (Ad5), which induces T-cell response, is a widely used viral vector. In this study, we aimed to evaluate the efficacy of a multi-antigenic recombinant Ad5 vectored vaccine and determine the optimal immunization route for enhanced immune response against Mycobacterium tuberculosis.
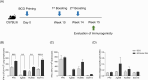
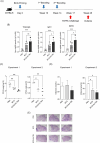
Methods: We constructed a multi-antigenic recombinant Ad5 vectored vaccine expressing four antigens (Ag85B-ESAT6-MPT64-Rv2660c) of M. tuberculosis (rAd-TB4), immunized with rAd-TB4 (5 × 107 infectious virus units/mouse) twice at an interval of 4 weeks starting at 10 weeks after BCG priming, and evaluated its boosting efficacy in a BCG-primed mouse model, and determined the optimal immunization route.
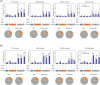
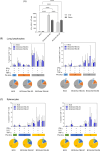
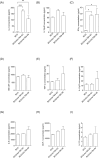
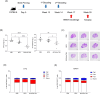
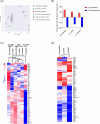
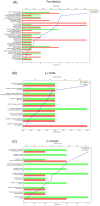
Results: Compared with the BCG-only (2 × 105 colony forming units/mouse), subcutaneous injection of rAd-TB4 (1 × 107 infectious virus units/mL; two doses) elicited a T-cell response and cytokine production in lung lymphocytes and splenocytes. rAd-TB4 immunization significantly reduced bacterial loads and inflamed lung areas compared to BCG immunization (p < 0.01) and protected against the H37Rv challenge performed at 17 weeks of BCG priming. RNA sequencing of the whole blood of rAd-TB4-vaccinated mice collected pre- and, 1 and 4 weeks post-infection, identified differentially expressed genes associated with immune and inflammatory responses, especially those in the Wnt signaling pathway.
Conclusion: Our results indicate that rAd-TB4 immunization enhances the immune response to the vaccine boosting antigens in BCG-primed mice, making it a potential adult pulmonary TB vaccine candidate.
Keywords: BCG vaccine; adenovirus vector; immune response; immunization; mouse model; multi-antigenic vaccine; pulmonary tuberculosis.
Copyright © 2025 Yun, Shin, Lee, Lee, Lee, Kim, Shin, Ha, Lee, Kim, Yoo and Jeong.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Abubakar I., Pimpin L., Ariti C., Beynon R., Mangtani P., Sterne J. A., et al. (2013). Systematic review and meta-analysis of the current evidence on the duration of protection by bacillus Calmette-Guérin vaccination against tuberculosis. Health Technol. Assess. 17 1–372. 10.3310/hta17370 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

