Prognostic and clinicopathological value of soluble programmed cell death ligand-1 (sPD-L1) in patients with peripheral T-cell lymphoma: a meta-analysis
- PMID: 39928126
- PMCID: PMC11812115
- DOI: 10.1080/07853890.2025.2458236
Prognostic and clinicopathological value of soluble programmed cell death ligand-1 (sPD-L1) in patients with peripheral T-cell lymphoma: a meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: Previous studies have explored whether soluble programmed cell death ligand-1 (sPD-L1) can be used to predict the prognosis of patients with peripheral T-cell lymphoma (PTCL); however, no consistent results have been obtained. Consequently, we conducted the present meta-analysis to identify the precise significance of sPD-L1 in predicting the prognosis of PTCL.
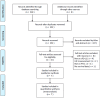
Methods: We searched PubMed, Embase, Web of Science, and the Cochrane Library until July 31, 2024. The value of sPD-L1 in predicting PTCL prognosis was examined by combining the hazard ratios (HRs) with 95% confidence intervals (CIs).
Results: Seven articles involving 445 patients were included in this study. Based on our pooled findings, increased sPD-L1 was associated with dismal overall survival (OS) (HR = 4.22, 95%CI = 1.89-9.43, p < 0.001) and worse progression-free survival (PFS) (HR = 2.57, 95%CI = 1.35-4.90, p = 0.004) in PTCL. Furthermore, higher sPD-L1 levels were correlated with male sex (OR = 1.80, 95%CI = 1.06-3.03, p = 0.029), International Prognostic Index (IPI) score ≥2 (OR = 4.32, 95%CI = 2.10-8.89, p < 0.001), elevated lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) level (OR = 5.15, 95%CI = 1.94-13.71, p = 0.001), presence of B symptoms (OR = 2.56, 95%CI = 1.45-4.52, p = 0.001), and ECOG PS ≥2 (OR = 7.41, 95%CI = 1.49-36.92, p = 0.015) in PTCL.
Conclusion: According to the present meta-analysis, higher sPD-L1 levels were significantly correlated with poor OS and inferior PFS in patients with PTCL. Additionally, high sPD-L1 levels were also associated with clinical features representing the development of PTCL.
Keywords: Soluble PD-L1; biomarker; meta-analysis; peripheral T-cell lymphoma; prognosis.
Plain language summary
The present meta-analysis has first explored the impact of sPD-L1 on forecasting PTCL prognosis.Higher sPD-L1 level was significantly correlated with dismal OS and inferior PFS of PTCL patients.High sPD-L1 was also connected to clinical features representing the disease development of PTCL.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the author(s).
Figures





References
-
- Stuver R, Epstein-Peterson ZD, Johnson WT, et al. . Current treatment of peripheral T-cell lymphoma. Oncology-New York. 2022;36(5):293–305. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
