Advances in controlled release drug delivery systems based on nanomaterials in lung cancer therapy: A review
- PMID: 39928802
- PMCID: PMC11813027
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000041415
Advances in controlled release drug delivery systems based on nanomaterials in lung cancer therapy: A review
Abstract
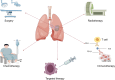
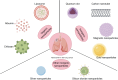
Lung cancer is one of the most common malignant tumors, with the highest morbidity and mortality rates. Currently, significant progress has been made in the treatment of lung cancer, which has effectively improved the overall prognosis of patients, but there are still many problems, such as tumor recurrence, drug resistance, and serious complications. With the rapid development of nanotechnology in the field of medicine, it breaks through the inherent limitations of traditional cancer treatments and shows great potential in tumor treatment. To address the drawbacks of traditional therapeutic means, nanodrug delivery systems can release drugs under specific conditions, thus realizing tumor-targeted drug delivery, which improves the antitumor effect of drugs. In this paper, we review the current treatments for lung cancer and further discuss the advantages and common carriers of nanodrug delivery systems. We also summarize the latest research progress of nanotargeted drug delivery systems in the field of lung cancer therapy, discuss the problems faced in their clinical translation, and look forward to future development opportunities and directions.
Copyright © 2025 the Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Advancing gastric cancer treatment: nanotechnology innovations and future prospects.Cell Biol Toxicol. 2024 Nov 20;40(1):101. doi: 10.1007/s10565-024-09943-9. Cell Biol Toxicol. 2024. PMID: 39565472 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Classification of stimuli-responsive polymers as anticancer drug delivery systems.Drug Deliv. 2015 Feb;22(2):145-55. doi: 10.3109/10717544.2014.887157. Epub 2014 Feb 19. Drug Deliv. 2015. PMID: 24547737 Review.
-
Enhanced therapeutic precision using dual drug-loaded nanomaterials for targeted cancer photodynamic therapy.Biomed Pharmacother. 2025 Mar;184:117909. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2025.117909. Epub 2025 Feb 11. Biomed Pharmacother. 2025. PMID: 39938348 Review.
-
Smart Drug-Delivery Systems for Cancer Nanotherapy.Curr Drug Targets. 2018 Feb 19;19(4):339-359. doi: 10.2174/1389450117666160527142544. Curr Drug Targets. 2018. PMID: 27231107 Review.
-
The Design and Application of Nanomaterials as Drug Carriers in Cancer Treatment.Curr Med Chem. 2020;27(36):6112-6135. doi: 10.2174/0929867326666190816231409. Curr Med Chem. 2020. PMID: 31419927 Review.
References
-
- Bray F, Laversanne M, Sung H, et al. . Global cancer statistics 2022: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2024;74:229–63. - PubMed
-
- Guo X, Zhuang Q, Ji T, et al. . Multi-functionalized chitosan nanoparticles for enhanced chemotherapy in lung cancer. Carbohydr Polym. 2018;195:311–20. - PubMed
-
- Chan MH, Huang WT, Wang J, Liu RS, Hsiao M. Next-generation cancer-specific hybrid theranostic nanomaterials: MAGE-A3 NIR persistent luminescence nanoparticles conjugated to afatinib for in situ suppression of lung adenocarcinoma growth and metastasis. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2020;7:1903741. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical