Inflammation in preschool cystic fibrosis is of mixed phenotype, extends beyond the lung and is differentially modified by CFTR modulators
- PMID: 39929713
- PMCID: PMC12322466
- DOI: 10.1136/thorax-2024-221634
Inflammation in preschool cystic fibrosis is of mixed phenotype, extends beyond the lung and is differentially modified by CFTR modulators
Abstract
Background: Early-life inflammation has long been recognised as a key pathophysiological process in the evolution of cystic fibrosis (CF) lung disease. Despite this, no CF-specific anti-inflammatory treatments have been developed. This is crucial even in the era of highly effective modulator therapy as recent evidence suggests that modulators alter, but may not fully resolve, pulmonary inflammation.
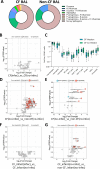
Methods: In this study, we used clinical microbiology data, high-dimensional flow cytometry and multiplex immunoassays to compare pulmonary (bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL)) and systemic immunity in 70 preschool children with CF and a total of 32 age-matched preschool controls.
Results: We show that inflammation in the early-life CF lung is characterised by innate cell infiltration (neutrophils: 31.31 vs 1.8% of BAL in CF compared with controls, FDRp=0.0001; eosinophils: 0.55 vs 0.06%, FDRp=0.001, and monocytes: 1.91 vs 0.45%, FDRp=0.004) and widespread upregulation of both traditional and type 2 inflammatory soluble signatures (40 analytes significantly elevated in BAL of CF compared with controls, all FDRp<0.1). Key targetable features of this response included pulmonary interleukin (IL)-8 and IL-13 which were most significantly associated with neutrophilic and eosinophilic infiltration, respectively (IL-8 and neutrophils; Spearman rho=0.68, FDRp=0.002: IL-13 and eosinophils; Spearman rho=0.75, FDRp=0.01). Signatures of type 2 inflammation, as identified by REACTOME pathway analysis, including IL-4, IL-13 and FGF-2, were highly elevated in both the lungs and circulation in early CF. When exploring the efficacy of Cystic Fibrosis Transmembrane Conductance Regulator modulators to resolve pulmonary and systemic inflammation in early life, we showed that different classes of modulators have varying effects on inflammation, with ivacaftor showing a more significant effect in the lungs and circulation than lumacaftor/ivacaftor. Finally, we showed that CF children with pathogen colonisation had similar levels of pulmonary inflammation as CF children without pathogen colonisation (no significant differences), and that inflammation was evident during infancy even without evidence of colonisation (as observed by significant increases in levels of SDF-1alpha, M-CSF, IL-2, IL-9, IL-12p40, IL-17, MCP-1 and LIGHT/TNFSF14, all FDRp<0.1), highlighting a role for intrinsic dysregulation of inflammation that begins in early life.
Conclusions: We provide a rationale for targeted anti-inflammatory intervention in early-life CF.
Keywords: Allergic lung disease; Cystic Fibrosis; Cytokine Biology; Innate Immunity; Paediatric Lung Disaese.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2025. Re-use permitted under CC BY. Published by BMJ Group.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures



References
-
- Cystic Fibrosis Foundation Drug development pipeline. 2023. [20-Sep-2023]. https://apps.cff.org/trials/pipeline Available. Accessed.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
