Randomized controlled trial of bromelain and alpha-lipoic acid in breast conservative surgery
- PMID: 39929877
- PMCID: PMC11811023
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-86651-2
Randomized controlled trial of bromelain and alpha-lipoic acid in breast conservative surgery
Abstract
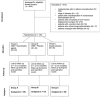
Aim of study is to analyze Bromelain' effects on the most common early complications after BCS (oedema and seroma). From January 2021 to December 2023 a double-blind randomized placebo-controlled trial was performed on 114 candidates for BCS at our Academic Unit. Group A received a supplement of Casperome™-Boswellia Phytosome® + Bromelain (CBB) in combination with alpha-lipoic acid + superoxide dismutase + B and D vitamins + centella asiatica. Group B received a supplement of CBB + placebo. Group C received placebo. The therapies were administrated for 30 days. On GEE logistic regression, drugs combination in A seems to be associated with statistical fewer oedema compared with C (P = 0.018 at 1 day and P = 0.002 after 1 month). Comparing B to C, B gained a significative value after 1 month (P = 0.007). On GEE logistic regression, the drugs combination in A has been associated with statistical fewer seroma compared with C (P = 0.009 at 15thpostoperative day and P < 0.001 after 1 month). B vs C reaches significant values 15 day and 1 month after surgery (P = 0.002 and P < 0.001, respectively). The current study is the first analyzing the employment of CBB association with/without neurotrophic agent on prevention of early complications after BCS.
Keywords: Breast cancer; Breast conserving surgery; Breast oedema; Breast seroma; Early complications; Post-surgical pain; Surgical outcomes.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Bertozzi, N., Pesce, M., Santi, P. L. & Raposio, E. Oncoplastic breast surgery: Comprehensive review. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci.21(11), 2572–2585 (2017). - PubMed
-
- Haloua, M. H. et al. A systematic review of oncoplastic breast-conserving surgery: Current weaknesses and future prospects. Ann. Surg.257(4), 609–620. 10.1097/SLA.0b013e3182888782 (2013). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical