Genome-wide association study of prostate-specific antigen levels in 392,522 men identifies new loci and improves prediction across ancestry groups
- PMID: 39930085
- PMCID: PMC11821537
- DOI: 10.1038/s41588-024-02068-z
Genome-wide association study of prostate-specific antigen levels in 392,522 men identifies new loci and improves prediction across ancestry groups
Abstract
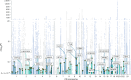
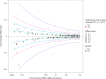
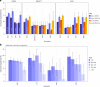
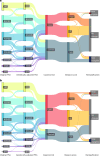
We conducted a multiancestry genome-wide association study of prostate-specific antigen (PSA) levels in 296,754 men (211,342 European ancestry, 58,236 African ancestry, 23,546 Hispanic/Latino and 3,630 Asian ancestry; 96.5% of participants were from the Million Veteran Program). We identified 318 independent genome-wide significant (P ≤ 5 × 10-8) variants, 184 of which were novel. Most demonstrated evidence of replication in an independent cohort (n = 95,768). Meta-analyzing discovery and replication (n = 392,522) identified 447 variants, of which a further 111 were novel. Out-of-sample variance in PSA explained by our genome-wide polygenic risk scores ranged from 11.6% to 16.6% for European ancestry, 5.5% to 9.5% for African ancestry, 13.5% to 18.2% for Hispanic/Latino and 8.6% to 15.3% for Asian ancestry and decreased with increasing age. Midlife genetically adjusted PSA levels were more strongly associated with overall and aggressive prostate cancer than unadjusted PSA levels. Our study highlights how including proportionally more participants from underrepresented populations improves genetic prediction of PSA levels, offering potential to personalize prostate cancer screening.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: J.S.W. and C.L.C. are nonemployee co-founders of Avail Bio. H.L. is named on a patent for intact PSA assays and a patent for a statistical method to detect prostate cancer that is licensed to and commercialized by OPKO Health. H.L. receives royalties from sales of the test and has stock in OPKO Health. J.S.W. consults for DLA Piper on subject matter unrelated to this study. R.E.G. consults for Hunton Andrews Kurth on subject matter unrelated to this study. The other authors declare no competing interests.
Figures






Update of
-
Genome-wide association study of prostate-specific antigen levels in 392,522 men identifies new loci and improves cross-ancestry prediction.medRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Aug 20:2023.10.27.23297676. doi: 10.1101/2023.10.27.23297676. medRxiv. 2024. Update in: Nat Genet. 2025 Feb;57(2):334-344. doi: 10.1038/s41588-024-02068-z. PMID: 37961155 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
-
- Lilja, H., Ulmert, D. & Vickers, A. J. Prostate-specific antigen and prostate cancer: prediction, detection and monitoring. Nat. Rev. Cancer8, 268–278 (2008). - PubMed
-
- Balk, S. P., Ko, Y.-J. & Bubley, G. J. Biology of prostate-specific antigen. J. Clin. Oncol.21, 383–391 (2003). - PubMed
-
- Pinsky, P. F. et al. Prostate volume and prostate-specific antigen levels in men enrolled in a large screening trial. Urology68, 352–356 (2006). - PubMed
-
- Lee, S. E. et al. Relationship of prostate-specific antigen and prostate volume in Korean men with biopsy-proven benign prostatic hyperplasia. Urology71, 395–398 (2008). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- RC2 AG036607/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- OT2 OD026556/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA241410/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA014599/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- OT2 OD026551/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- U24 OD023121/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- OT2 OD025337/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA008748/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- OT2 OD025277/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- OT2 OD026555/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- OT2 OD026550/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- OT2 OD026553/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- OT2 OD023205/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- S10 OD030463/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- OT2 OD026557/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- OT2 OD026554/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- U24 OD023163/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 CA182883/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U24 OD023176/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA037429/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- OT2 OD026548/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001863/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- U2C OD023196/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA244948/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- OT2 OD025315/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- OT2 OD026552/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- U01 CA261339/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- OT2 OD026549/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- R00 CA246076/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- S10 OD026880/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA175491/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 CA266535/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 CA184374/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- OT2 OD025276/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- OT2 OD023206/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM130791/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

