Targeting CDK4/6 in breast cancer
- PMID: 39930131
- PMCID: PMC11873051
- DOI: 10.1038/s12276-025-01395-3
Targeting CDK4/6 in breast cancer
Abstract
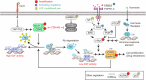
Dysregulation of the cell cycle machinery, particularly the overactivation of cyclin-dependent kinases 4 and 6 (CDK4/6), is a hallmark of breast cancer pathogenesis. The introduction of CDK4/6 inhibitors has transformed the treatment landscape for hormone receptor-positive breast cancer by effectively targeting abnormal cell cycle progression. However, despite their initial clinical success, drug resistance remains a significant challenge, with no reliable biomarkers available to predict treatment response or guide strategies for managing resistant populations. Consequently, numerous studies have sought to investigate the mechanisms driving resistance to optimize the therapeutic use of CDK4/6 inhibitors and improve patient outcomes. Here we examine the molecular mechanisms regulating the cell cycle, current clinical applications of CDK4/6 inhibitors in breast cancer, and key mechanisms contributing to drug resistance. Furthermore, we discuss emerging predictive biomarkers and highlight potential directions for overcoming resistance and enhancing therapeutic efficacy.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Hanahan, D. Hallmarks of cancer: new dimensions. Cancer Discov.12, 31–46 (2022). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- P30 CA013696/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- V2023-017/V Foundation for Cancer Research (V Foundation)
- RSG-22-101-01-CDP/American Cancer Society (American Cancer Society, Inc.)
- P30-CA013696/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | National Institutes of Health (NIH)
- R01 GM145884/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

