Curcumin attenuates myocardial ischemia‑reperfusion‑induced autophagy‑dependent ferroptosis via Sirt1/AKT/FoxO3a signaling
- PMID: 39930816
- PMCID: PMC11781526
- DOI: 10.3892/ijmm.2025.5492
Curcumin attenuates myocardial ischemia‑reperfusion‑induced autophagy‑dependent ferroptosis via Sirt1/AKT/FoxO3a signaling
Abstract
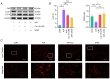
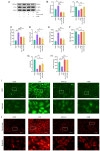
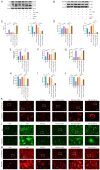
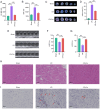
Curcumin (Cur) effectively attenuates myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury (MIRI). MIRI has a complex mechanism and is associated with autophagy‑dependent ferroptosis. Therefore, the present study aimed to determine whether autophagy‑dependent ferroptosis occurs in MIRI and assess the mechanism of Cur in attenuating MIRI. The study was conducted on a Sprague‑Dawley rat MIRI model and H9c2 cell anoxia/reoxygenation (A/R) injury model. The effect of Cur pretreatment on A/R or MIRI induced autophagy‑dependent ferroptosis and its molecular mechanism were investigated. Protein expression, lysosomal, reactive oxygen species, Fe2+, oxidative systems, mitochondrial function, subcellular localization of molecules, and cardiac function assays will be employed. Cur decreased MIRI; improved myocardial histopathology; increased cardiomyocyte viability; inhibited ferroptosis, apoptosis and autophagy; reduced infarct size and maintained cardiac function. MIRI decreased silent information regulator 1 (Sirt1), decreased AKT and forkhead box O3A (FoxO3a) phosphorylation, leading to FoxO3a entry into the nucleus to activate translation of autophagy‑related genes and inducing ferroptosis, apoptosis and autophagy. However, Cur pretreatment activated AKT and FoxO3a phosphorylation via Sirt1, thereby transporting FoxO3a out of the nucleus, reducing autophagy‑related gene translation and attenuating MIRI‑induced ferroptosis, apoptosis and autophagy. Of note, the silencing of Sirt1 and administration of triciribine (an AKT inhibitor) both eliminated the protective effect of Cur. Thus, Cur maintained cardiomyocyte function by inhibiting autophagy‑dependent ferroptosis via Sirt1/AKT/FoxO3a signaling.
Keywords: Silent information regulator 1; autophagy; curcumin; ferroptosis; myocardial ischemia/reperfusion.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures




References
-
- Hausenloy DJ, Garcia-Dorado D, Bøtker HE, Davidson SM, Downey J, Engel FB, Jennings R, Lecour S, Leor J, Madonna R, et al. Novel targets and future strategies for acute cardioprotection: Position paper of the european society of cardiology working group on cellular biology of the heart. Cardiovasc Res. 2017;113:564–585. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvx049. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
