Case report: Chemotherapy plus sintilimab for the treatment of gastroesophageal junction hepatoid adenocarcinoma with liver metastasis: a case study with literature review
- PMID: 39931054
- PMCID: PMC11808132
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1513604
Case report: Chemotherapy plus sintilimab for the treatment of gastroesophageal junction hepatoid adenocarcinoma with liver metastasis: a case study with literature review
Abstract
Objective: To elucidate the clinicopathological features and treatment of metastatic gastroesophageal junction hepatoid adenocarcinoma (GEJ HAC)using a case study and literature review.
Methods: Clinical presentation, results of histology and immunohistochemistry, and next-generation sequencing(NGS) in a patient with GEJ HAC metastasizing to the liver were reviewed. Chemotherapy (SOX or S-1) plus sintilimab was administered.
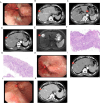
Results: A 65-year-old male patient with a history of hypertension was admitted to the hospital due to a one-week increase in serum AFP levels. There was a small intraluminal mass at the GEJ and a metastatic lesion in liver segment VIII, as well as enlarged perigastric and retroperitoneal lymph nodes. Tumor cells in both the GEJ and liver tissue exhibited a glandular shape with a nest-like adenoid structure. Immunohistochemical (IHC) analysis of the GEJ tissue showed positivity for AFP, CA19-9, CK7, CK20, MUC-1, P53 (wild type), Glypican-3, and HepPar-1, and negativity for Arginase-1, CD10, and Her-2. In the metastatic liver tissue, IHC testing demonstrated positivity for AFP, CD10, CK19, CK20, HepPar-1, MUC-1, Ki-67, and P53 (wild type), while CK7 was negative. The NGS report of GEJ mass indicated that the JAK2 and TP53 genes harbored missense mutations, while the MLH1, MSH2, MSH6, PMS2, ERBB2, EGFR, PIK3CA, APC, CTNNB1, CDH1, and DPYD genes were normal. The patient's serum levels of CEA, CA19-9, and AFP were sharply decreased. The patient achieved a major pathological response (MPR) and remains in a progression-free stage.
Conclusions: Sintilimab-based chemotherapy has proven efficacy in achieving a MPR and maintaining a progression-free state for a patient with GEJ HAC that has metastasized to the liver.
Keywords: chemotherapy; gastroesophageal junction; hepatoid adenocarcinoma; liver metastasis; sintilimab.
Copyright © 2025 Lu, Tu, Tu and Jiang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Nagai Y, Kato T, Harano M, Satoh D, Choda Y, Tokumoto N, et al. . A case of AFP-producing esophagogastric junction cancer with liver metastases with a good response to chemotherapy. Gan To Kagaku Ryoho. (2014) 41:2349–51. - PubMed
-
- Apostolou K, Schizas D, Vergadis C, Vailas M, Ptohis N, Liakakos T. Primary adenocarcinoma of the esophagogastric junction, combined with an obscure hepatoid adenocarcinoma component, as discovered after the development of a metachronous liver metastasis. Hippokratia. (2020) 24:138–42. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Gálvez-Muñoz E, Gallego-Plazas J, Gonzalez-Orozco V, Menarguez-Pina F, Ruiz-Maciá JA, Morcillo MA. Hepatoid adenocarcinoma of the stomach - a different histology for not so different gastric adenocarcinoma: a case report. Int Semin Surg Oncol. (2009) 6:13. doi: 10.1186/1477-7800-6-13 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

