Gut Microecological Prescription: A Novel Approach to Regulating Intestinal Micro-Ecological Balance
- PMID: 39931312
- PMCID: PMC11807788
- DOI: 10.2147/IJGM.S504616
Gut Microecological Prescription: A Novel Approach to Regulating Intestinal Micro-Ecological Balance
Abstract
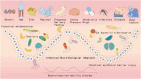
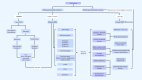
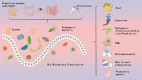
The intestinal microecology is comprises intestinal microorganisms and other components constituting the entire ecosystem, presenting characteristics of stability and dynamic balance. Current research reveals intestinal microecological imbalances are related to various diseases. However, fundamental research and clinical applications have not been effectively integrated. Considering the importance and complexity of regulating the intestinal microecological balance, this study provides an overview of the high-risk factors affecting intestinal microecology and detection methods. Moreover, it proposes the definition of intestinal microecological imbalance and the definition, formulation, and outcomes of gut microecological prescription to facilitate its application in clinical practice, thus promoting clinical research on intestinal microecology and improving the quality of life of the population.
Keywords: definition; faecal microbiota transplantation; gut microecological prescription; intestinal microecology; risk.
© 2025 Zhu and Yang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Research status of the relationship between microecological imbalance and lung cancer.Front Microbiol. 2025 Mar 10;16:1558379. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2025.1558379. eCollection 2025. Front Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 40130240 Free PMC article. Review.
-
An update on the effects of food-derived active peptides on the intestinal microecology.Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2023 Nov;63(33):11625-11639. doi: 10.1080/10408398.2022.2094889. Epub 2022 Jul 6. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2023. PMID: 35791779 Review.
-
Dietary olive oil enhances the oral tolerance of the food allergen ovalbumin in mice by regulating intestinal microecological homeostasis.J Food Biochem. 2022 Oct;46(10):e14297. doi: 10.1111/jfbc.14297. Epub 2022 Jul 2. J Food Biochem. 2022. PMID: 35780313
-
Different Effects of Premature Infant Formula and Breast Milk on Intestinal Microecological Development in Premature Infants.Front Microbiol. 2020 Jan 17;10:3020. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2019.03020. eCollection 2019. Front Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 32010090 Free PMC article.
-
[Research progress on intestinal microecology regulating mechanism and biological activities of polysaccharides].Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2021 Nov;46(21):5585-5592. doi: 10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm.20210623.701. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2021. PMID: 34951210 Review. Chinese.
Cited by
-
Dose-dependent effects of capsaicin on intestinal morphology and microbiota composition in mice: Structural, immunohistochemical, and microbial insights.Vet World. 2025 Jun;18(6):1703-1714. doi: 10.14202/vetworld.2025.1703-1714. Epub 2025 Jun 26. Vet World. 2025. PMID: 40689185 Free PMC article.
-
From Microbial Ecology to Clinical Challenges: The Respiratory Microbiome's Role in Antibiotic Resistance.Pathogens. 2025 Apr 5;14(4):355. doi: 10.3390/pathogens14040355. Pathogens. 2025. PMID: 40333133 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Editorial: Improve immunity against infection and tumor by regulating gut microbiota.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2025 May 29;15:1546123. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2025.1546123. eCollection 2025. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 40510798 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources