Effectiveness and safety profile of mesenchymal stem cell secretome as a treatment for severe cases of COVID-19: a randomized controlled trial
- PMID: 39931658
- PMCID: PMC11809480
- DOI: 10.12688/f1000research.75580.2
Effectiveness and safety profile of mesenchymal stem cell secretome as a treatment for severe cases of COVID-19: a randomized controlled trial
Abstract
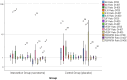
Background: : Patients with severe COVID-19 had a higher increase in pro-inflammatory and anti-inflammatory cytokines than patients with moderate COVID-19. Excessive release of cytokine and chemokines can lead to multi-organ failure, increasing disease severity, length of stay, and mortality rate. Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) are known to have immunomodulatory, anti-inflammatory, anti-apoptotic, and angiogenesis effects that are useful for relieving inflammation, recovery, and protection of lung tissues in COVID-19 patients. Secretome, a secretory product of MSCs, has several advantages over MSCs. Therefore, we conducted a study to investigate secretomes' effectiveness and safety profile as a treatment for severe COVID-19. Methods: This study was a double-blind, multicentered, randomized, placebo-controlled trial. This study involved 40 subjects recruited from three top COVID-19 referral hospitals in the Greater Jakarta area, Indonesia. Eligible subjects (n=40) were randomized in a 1:1 ratio to intervention group (n=20) and a control group (n=20). The primary outcome of this study was the improvement of inflammatory markers levels, measured by changes in inflammatory markers, and ratio of inflammatory to anti-inflammatory markers. The secondary outcomes of this study included clinical outcome, laboratory outcome, radiological outcome, RT-PCR result conversion, and safety profile of MSC secretome. Results: IL-6 marker in the control group was increased on the 14 th day after the intervention compared to before intervention [4.110 (2.403-12.820) at baseline to 13.320 (2.958-33.285) on 14 th day after intervention, p=0.017]. In the intervention group, there was no increase in the IL-6/IL-10 ratio. In contrast, in the control group, there was a significant increase in the IL-6/IL-10 ratio (p=0.036) on the 14 th day after the intervention compared to before the intervention. We also found that on the seventh day after the intervention, most of the subjects who received placebo had high levels of IL-6 and ferritin (p=0.043). There was no significant difference in the laboratory outcome, radiological outcome, RT-PCR result conversion, and safety profile between both groups. Conclusions: Our study showed an increase of inflammation markers in the control group on the 14 th day after the intervention, compared to the intervention group. The ratio of inflammatory to anti-inflammatory markers on the seventh and 14 th days after intervention also did not increase in the intervention group. On the seventh day after intervention, most of the subjects in the control group also had high IL-6 levels and high ferritin levels. There is no adverse event reported. MSC secretome is a safe and promising treatment modality for severe COVID-19.
Keywords: COVID-19; cytokine; inflammation mediators; mesenchymal stem cell; secretome.
Copyright: © 2022 Abdullah M et al.
Conflict of interest statement
No competing interests were disclosed.Murdani Abdullah, Ismail Hadisoebroto Dilogo, Jeanne Adiwinata Pawitan, Cosphiadi Irawan, Rahyussalim, Dita Aditianingsih, Isabella Kurnia Liem, Robert Sinto, Adityo Susilo, Mira Yulianti, Raden Rara Diah Handayani, Erlina Burhan, Triya Damayanti, Irandi Putra Pratomo, Herry Wibowo stated that there were no competing interests.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

