Novel Therapeutic Approach Targeting CXCR3 to Treat Immunotherapy Myocarditis
- PMID: 39931812
- PMCID: PMC11867805
- DOI: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.124.325652
Novel Therapeutic Approach Targeting CXCR3 to Treat Immunotherapy Myocarditis
Abstract
Background: Immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) are successful in treating many cancers but may cause immune-related adverse events. ICI-mediated myocarditis has a high fatality rate with severe cardiovascular consequences. Targeted therapies for ICI myocarditis are currently limited.
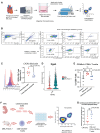
Methods: We used a genetic mouse model of PD1 deletion (MRL/Pdcd1-/-) along with a novel drug-treated ICI myocarditis mouse model to recapitulate the disease phenotype. We performed single-cell RNA-sequencing, single-cell T-cell receptor sequencing, and cellular indexing of transcriptomes and epitopes on immune cells isolated from MRL and MRL/Pdcd1-/- mice at serial time points. We assessed the impact of macrophage deletion in MRL/Pdcd1-/- mice, then inhibited CXCR3 (C-X-C motif chemokine receptor 3) in ICI-treated mice to assess the therapeutic effect on myocarditis phenotype. Furthermore, we delineated the functional and mechanistic effects of CXCR3 blockade on T-cell and macrophage interactions. We then correlated the results in human single-cell multiomics data from blood and heart biopsy data from patients with ICI myocarditis.
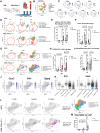
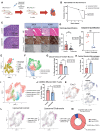
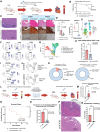
Results: Single-cell multiomics demonstrated expansion of CXCL (C-X-C motif chemokine ligand) 9/10+CCR2+ macrophages and CXCR3hi (C-X-C motif chemokine receptor 3 high-expressing) CD8+ (cluster of differentiation) effector T lymphocytes in the hearts of MRL/Pdcd1-/- mice correlating with onset of myocarditis development. Both depletion of CXCL9/10+CCR2+ (C-C motif chemokine receptor) macrophages and CXCR3 blockade, respectively, led to decreased CXCR3hi CD8+ T-cell infiltration into the heart and significantly improved survival. Transwell migration assays demonstrated that the selective blockade of CXCR3 and its ligand, CXCL10, reduced CXCR3+CD8+ T-cell migration toward macrophages, implicating this interaction in T-cell cardiotropism toward cardiac macrophages. Furthermore, cardiomyocyte apoptosis was induced by CXCR3hi CD8+ T cells. Cardiac biopsies from patients with confirmed ICI myocarditis demonstrated infiltrating CXCR3+ T cells and CXCL9+/CXCL10+ macrophages. Both mouse cardiac immune cells and patient peripheral blood immune cells revealed expanded TCRs (T-cell receptors) correlating with CXCR3hi CD8+ T cells in ICI myocarditis samples.
Conclusions: These findings bring forth the CXCR3-CXCL9/10 axis as an attractive therapeutic target for ICI myocarditis treatment, and more broadly as a druggable pathway in cardiac inflammation.
Keywords: T-lymphocytes; chemokines; immune checkpoint inhibitors; macrophages; myocarditis.
Conflict of interest statement
H.A. Wakelee is an advisory board participant of IOBiotech and Mirati, and she does unpaid consultant work at Bristol Meyers Squibb (BMS), Genentech/Roche, Merck, and AstraZeneca. She receives clinical trial support from AstraZeneca/MedImmune, Bayer, BMS, Genentech/Roche, Helsinn, Merck, SeaGen, and Xcovery. Dr. Neal has received honoraria from Continuing Medical Education (CME) Matters, Clinical Care Options CME, Research to Practice CME, Medscape CME, Biomedical Learning Institute CME, Medical Learning Institute (MLI) Peerview CME, Prime Oncology CME, Projects in Knowledge CME, Rockpointe CME, MJH Life Sciences CME, Medical Educator Consortium, and Healthcare Management Perspectives (HMP) Education. He is a consultant at AstraZeneca, Genentech/Roche, Exelixis, Takeda Pharmaceuticals, Eli Lilly and Company, Amgen, Iovance Biotherapeutics, Blueprint Pharmaceuticals, Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Natera, Sanofi/Regeneron, D2G Oncology, Surface Oncology, Turning Point Therapeutics, Mirati Therapeutics, Gilead Sciences, Abbvie, Summit Therapeutics, Novartis, Novocure, Janssen Oncology, and Anheart Therapeutics. He receives research funding from Genentech/Roche, Merck, Novartis, Boehringer Ingelheim, Exelixis, Nektar Therapeutics, Takeda Pharmaceuticals, Adaptimmune, GSK, Janssen, AbbVie, and Novocure. G.J. Berry has received honoraria from Merck Pharmaceuticals for lectures on lung cancer biomarker testing for patients receiving pembrolizumab. S. Waliany is a consultant at AstraZeneca. The other authors report no conflicts.
Figures

References
-
- Waliany S, Lee D, Witteles RM, Neal JW, Nguyen P, Davis MM, Salem JE, Wu SM, Moslehi JJ, Zhu H. Immune checkpoint inhibitor cardiotoxicity: understanding basic mechanisms and clinical characteristics and finding a cure. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 2021;61:113–134. doi: 10.1146/annurev-pharmtox-010919-023451 - PubMed
-
- Wahli MN, Hayoz S, Hoch D, Ryser CO, Hoffmann M, Scherz A, Schwacha-Eipper B, Häfliger S, Wampfler J, Berger MD, et al. . The role of immune checkpoint inhibitors in clinical practice: an analysis of the treatment patterns, survival and toxicity rates by sex. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2023;149:3847–3858. doi: 10.1007/s00432-022-04309-2 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Waliany S, Neal JW, Reddy S, Wakelee H, Shah SA, Srinivas S, Padda SK, Fan AC, Colevas AD, Wu SM, et al. . Myocarditis surveillance with high-sensitivity troponin I during cancer treatment with immune checkpoint inhibitors. JACC CardioOncol. 2021;3:137–139. doi: 10.1016/j.jaccao.2021.01.004 - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

