Tribbles Pseudokinase 3 Converts Sorafenib Therapy to Neutrophil-Mediated Lung Metastasis in Hepatocellular Carcinoma
- PMID: 39932456
- PMCID: PMC11967757
- DOI: 10.1002/advs.202413682
Tribbles Pseudokinase 3 Converts Sorafenib Therapy to Neutrophil-Mediated Lung Metastasis in Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Abstract
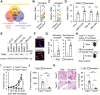
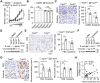
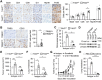
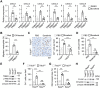
Rapid development of resistance to sorafenib and subsequent hyperprogression in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) pose significant challenges, with the underlying mechanisms still largely unknown. Herein, sorafenib-induced TRIB3 is identified as a liver-specific determinant driving secondary resistance to sorafenib by facilitating the accumulation of protumorigenic neutrophils within tumors. Mechanistically, TRIB3, triggered by the sorafenib-elicited ROS-ER stress axis, operates in an NF-κB-dependent manner to upregulate CXCR1/2 ligands, subsequently promoting neutrophil recruitment into tumors. These enriched neutrophils enhance epithelial-mesenchymal transition processes in malignant cells through the oncostatin M-STAT3 pathway, thereby repurposing the therapeutic efficacy of sorafenib away from anti-angiogenesis and toward lung metastasis. Clinically, elevated TRIB3 expression indicates inferior survival and unfavorable clinical efficacy of sorafenib in HCC patients. Correspondingly, strategies that either inhibiting TRIB3 upregulation or blocking its downstream signaling successfully augment the therapeutic efficacy of sorafenib and prevent sorafenib-induced hyperprogression in vivo. The study thus identifies a pivotal mechanism of sorafenib resistance in HCC, centered on the TRIB3-mediated recruitment of protumorigenic neutrophils and subsequent disease hyperprogression.
Keywords: TRIB3; hepatocellular carcinoma; lung metastasis; neutrophil; sorafenib resistance.
© 2025 The Author(s). Advanced Science published by Wiley‐VCH GmbH.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Craig A. J., von Felden J., Garcia‐Lezana T., Sarcognato S., Villanueva A., Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020, 17, 139. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 2023B1111030006/Key-Area Research and Development Program of Guangdong Province
- 32200740/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 82472868/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 82303902/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 2023A1515012463/Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province
- 2023A1515012466/Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province
- 2024A1515010549/Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province
- 2022A1515220220/Guangdong Provincial Basic and Applied Basic Research Fund Project Provincial Enterprise Joint Fund General Project
- 2020ycqd001/Research Start Project of Zhuhai People's Hospital
- 23ptpy61/Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities
- 2024A03J0101/Guangzhou Municipal Institute Enterprise Joint Funding Project
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
