Characterization of Plasma Cell-Free DNA Variants as of Tumor or Clonal Hematopoiesis Origin in 16,812 Advanced Cancer Patients
- PMID: 39932457
- PMCID: PMC12209822
- DOI: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-24-3335
Characterization of Plasma Cell-Free DNA Variants as of Tumor or Clonal Hematopoiesis Origin in 16,812 Advanced Cancer Patients
Abstract
Purpose: Plasma-based liquid biopsy tests can detect tumor-specific genetic alterations and offer many advantages that complement tissue-based comprehensive genomic profiling. However, age-related clonal hematopoiesis (CH) mutations can confound liquid biopsy results and potentially lead to incorrect therapy choice.
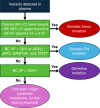
Experimental design: We assessed the landscape of 16,812 liquid profiles across 49 cancer types using the Caris Assure assay, a whole-exome and whole-transcriptome next-generation sequencing workflow that independently sequences both plasma-derived cell-free total nucleic acids and the white blood cell DNA and RNA from the buffy coat. The variant source was identified algorithmically by comparing plasma and buffy coat variant frequency and read quality metrics.
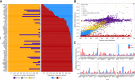
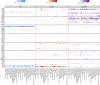
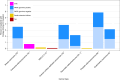
Results: Of 16,812 patients, 42.3% presented at least one CH variant among reportable clinical genes. We found 39% of BRCA2 variants to be of CH origin, as well as 37.9% of CHEK2, 27.4% of BRCA1, 20.1% of ATM, 7.3% of NRAS, 5.8% of BRAF, 2.1% of EGFR, 2.1% of KRAS, and 18.5% of TP53. For patients aged 65 to 69 years, the median proportion of CH variant classification was 20%, whereas it was 33% for patients aged 70 to 74 years, 33% for ages 75 to 79 years, and 50% for ages 80+ years. We found high rates of CH detected in what would be otherwise druggable targets in many cancer types typically treated with PARP inhibitors, including breast, female genital tract, ovarian, pancreatic, prostate, and endometrial cancers.
Conclusions: This large study highlights the need for thorough CH classification during liquid biopsy to appropriately recommend therapies, especially PARP inhibitors. See related commentary by Bernard and Micol, p. 2545.
©2025 The Authors; Published by the American Association for Cancer Research.
Conflict of interest statement
D. Magee reports other support from Caris Life Sciences during the conduct of the study, as well as employment with and stock ownership in Caris Life Sciences. V. Domenyuk reports other support from Caris Life Sciences outside the submitted work. J. Abraham reports other support from Caris Life Sciences during the conduct of the study, as well as other support from Caris Life Sciences outside the submitted work. N. Perdigones Borderias reports other support from Caris Life Sciences outside the submitted work. J. Swensen reports other support from Caris Life Sciences during the conduct of the study. A.F. Shields reports personal fees and other support from Caris Life Sciences outside the submitted work. J.R. Ribeiro reports personal fees from Caris Life Sciences during the conduct of the study, as well as personal fees from Caris Life Sciences outside the submitted work. R. Hahn-Lowry reports other support from Caris Life Sciences during the conduct of the study, as well as being employed with Caris Life Sciences and holding equity in Caris Life Sciences. G.W. Sledge reports other support from Caris Life Sciences outside the submitted work. M. Oberley reports other support from Caris Life Sciences outside the submitted work. M. Radovich reports personal fees from Caris Life Sciences during the conduct of the study, as well as personal fees from Caris Life Sciences outside the submitted work. No disclosures were reported by the other authors.
Figures
References
-
- Prabhash K, Biswas B, Khurana S, Batra U, Biswas G, Advani SH, et al. CONCORDANCE: a real-world evidence study to evaluate the concordance of detecting epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) mutation by circulating tumor DNA* versus tissue biopsy in patients with metastatic non-small cell lung cancer. Indian J Cancer 2022;59(Suppl):S11–18. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

