Phosphorylation of CRYAB induces a condensatopathy to worsen post-myocardial infarction left ventricular remodeling
- PMID: 39932799
- PMCID: PMC11957698
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI163730
Phosphorylation of CRYAB induces a condensatopathy to worsen post-myocardial infarction left ventricular remodeling
Abstract
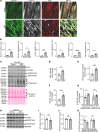
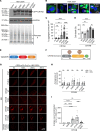
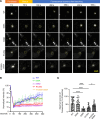
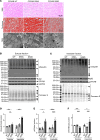
Protein aggregates are emerging therapeutic targets in rare monogenic causes of cardiomyopathy and amyloid heart disease, but their role in more prevalent heart-failure syndromes remains mechanistically unexamined. We observed mislocalization of desmin and sarcomeric proteins to aggregates in human myocardium with ischemic cardiomyopathy and in mouse hearts with post-myocardial infarction ventricular remodeling, mimicking findings of autosomal-dominant cardiomyopathy induced by the R120G mutation in the cognate chaperone protein CRYAB. In both syndromes, we demonstrate increased partitioning of CRYAB phosphorylated on serine 59 to NP40-insoluble aggregate-rich biochemical fraction. While CRYAB undergoes phase separation to form condensates, the phosphomimetic mutation of serine 59 to aspartate (S59D) in CRYAB mimics R120G-CRYAB mutants with reduced condensate fluidity, formation of protein aggregates, and increased cell death. Conversely, changing serine to alanine (phosphorylation-deficient mutation) at position 59 (S59A) restored condensate fluidity and reduced both R120G-CRYAB aggregates and cell death. In mice, S59D CRYAB knockin was sufficient to induce desmin mislocalization and myocardial protein aggregates, while S59A CRYAB knockin rescued left ventricular systolic dysfunction after myocardial infarction and preserved desmin localization with reduced myocardial protein aggregates. 25-Hydroxycholesterol attenuated CRYAB serine 59 phosphorylation and rescued post-myocardial infarction adverse remodeling. Thus, targeting CRYAB phosphorylation-induced condensatopathy is an attractive strategy to counter ischemic cardiomyopathy.
Keywords: Cardiology; Cardiovascular disease; Cell biology; Chaperones.
Figures


Update of
-
Phosphorylation of CRYAB Induces a Condensatopathy to Worsen Post-Myocardial Infarction Left Ventricular Remodeling.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Sep 3:2024.08.30.610556. doi: 10.1101/2024.08.30.610556. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: J Clin Invest. 2025 Feb 11;135(7):e163730. doi: 10.1172/JCI163730. PMID: 39282298 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 HL125838/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL159461/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL143431/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL107594/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R35 GM128772/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK056341/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- T32 HL007081/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- I01 BX005981/BX/BLRD VA/United States
- I01 BX005065/BX/BLRD VA/United States
- K08 HL163469/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK131188/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK020579/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- S10 OD028597/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- I01 BX003415/BX/BLRD VA/United States
- R01 NS094692/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL155344/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- K08 HL138262/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- I01 BX004235/BX/BLRD VA/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

