Mendelian randomization analysis to identify potential drug targets for osteoarthritis
- PMID: 39932908
- PMCID: PMC11813149
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0316824
Mendelian randomization analysis to identify potential drug targets for osteoarthritis
Abstract
Background: Osteoarthritis (OA) is a prevalent chronic joint disease for which there is a lack of effective treatments. In this study, we used Mendelian randomization analysis to identify circulating proteins that are causally associated with OA-related traits, providing important insights into potential drug targets for OA.
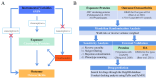
Method: Causal associations between 1553 circulating proteins and five OA-related traits were assessed in large-scale two-sample MR analyses using Wald ratio or inverse variance weighting, and the results were corrected for Bonferroni. In addition, sensitivity analyses were performed to validate the reliability of the MR results, including reverse MR analysis and Steiger filtering to ensure the causal direction between circulating proteins and OA; Bayesian co-localization and phenotypic scanning were used to eliminate confounding effects and horizontal pleiotropy. External validation was performed to exclude incidental findings using novel plasma protein quantitative trait loci. Finally, the online analysis tool Enrichr was utilized to screen drugs and molecular docking was performed to predict binding modes and energies between proteins and drugs to identify the most stable and likely binding modes and drugs.
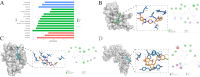
Result: Four proteins were ultimately found to be reliably and causally associated with three OA-related features: DNAJB12 and USP8 were associated with knee OA, IL12B with spinal OA, and RGMB with thumb OA. The ORs for the above proteins were 1.51 (95% CI, 1.26-1.81), 1.72 (95% CI, 1.42-2.08), 0.87 (95% CI, 0.81-0.92), and 0.59 (95% CI, 0.47-0.75), respectively. Drug-predicting small molecules (doxazosin, XEN 103, and montelukast) that simultaneously target three proteins, DNAJB12, USP8, and IL12B, docked well.
Conclusion: Based on our comprehensive analysis, we can draw the conclusion that there is a causal relationship between the genetic levels of DNAJB12, USP8, IL12B, and RGMB and the risk of respective OA.They may be potential options for OA screening and prevention in clinical practice. They can also serve as candidate molecules for future mechanism exploration and drug target selection.
Copyright: © 2025 Lu et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Unraveling the relationship between obstructive sleep apnea and osteoarthritis: A multivariate mendelian randomization highlighting the role of BMI as a confounding factor.Exp Gerontol. 2025 Jan;199:112657. doi: 10.1016/j.exger.2024.112657. Epub 2024 Dec 17. Exp Gerontol. 2025. PMID: 39672284
-
Causal associations between circulating immune cells and osteoarthritis: A bidirectional mendelian randomization study.Int Immunopharmacol. 2024 Dec 5;142(Pt A):113156. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2024.113156. Epub 2024 Sep 15. Int Immunopharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39278062
-
Genetic association of gut microbiota with osteoarthritis: a multivariable Mendelian randomization study considering medication use.J Med Microbiol. 2024 Oct;73(10). doi: 10.1099/jmm.0.001920. J Med Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 39412235
-
Proteome-Wide Mendelian Randomization and Colocalization Analysis Identify Therapeutic Targets for Knee and Hip Osteoarthritis.Biomolecules. 2024 Mar 15;14(3):355. doi: 10.3390/biom14030355. Biomolecules. 2024. PMID: 38540773 Free PMC article.
-
Plasma lipids, alcohol intake frequency and risk of Osteoarthritis: a Mendelian randomization study.BMC Public Health. 2023 Jul 11;23(1):1327. doi: 10.1186/s12889-023-16250-1. BMC Public Health. 2023. PMID: 37434151 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Dt F, Rc L, Pa D, R H, Cg H, Jm J, et al.. Osteoarthritis: new insights. Part 1: the disease and its risk factors. Annals of internal medicine. 2000;133. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

