Public satisfaction with Healthy China Action Plan implementation: a web-based cross-sectional survey in southwest China
- PMID: 39933807
- PMCID: PMC11815437
- DOI: 10.1136/bmjopen-2024-091039
Public satisfaction with Healthy China Action Plan implementation: a web-based cross-sectional survey in southwest China
Abstract
Objective: The Healthy China (Guangxi) Action Plan has been in effect for approximately 4 years, with its primary goals being to improve public health and prevent diseases. However, there is limited information available on the community-level public satisfaction with the outcomes of its implementation. Therefore, we intend to conduct an assessment based in southwest China.
Design: A population-based, cross-sectional survey was performed between 1 June 2023 and 31 July 2023.
Setting: Community members of all 14 prefecture-level cities within Guangxi, China, during June 2023 to July 2023.
Participants: A total of 62 4016 participants were included for analysis based on exclusion criteria, with 44.4% aged 18-35 and a male to female ratio of 3:2.
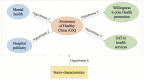
Primary outcome measure: 'Public satisfaction with the Healthy China (Guangxi) Action Plan implementation' was measured by the combination of 'Willingness to join health promotion' and 'Satisfaction to overall medical implementation measures and services' using a structural equation model with a multiple-indicator, multiple-cause approach in R software.
Results: The study proposed a comprehensive five-factor model to evaluate the public satisfaction with Healthy China (Guangxi) Action Plan implementation. With the mediator of 'awareness of Healthy China (Guangxi) Action Plan', health education/promotion demonstrated important effect on overall public satisfaction with Healthy China (Guangxi) Action Plan implementation. Mental health had small but positive effect on the outcomes. High socio-characteristic variables showed negative effects on all latent variables except for the mental health status. All of the effects were statistically significant.
Conclusions: Understanding the impact of background variables on public satisfaction with Healthy China (Guangxi) Action Plan implementation was crucial, along with considering the sociodemographic traits of participants. This knowledge helped policymakers to develop tailored interventions and strategies.
Keywords: Awareness; Health policy; PUBLIC HEALTH; Patient Satisfaction.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2025. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ Group.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Assessment of health promotion action for tuberculosis of end tuberculosis action plan (2019-2022) in China.BMC Public Health. 2024 Jul 30;24(1):2051. doi: 10.1186/s12889-024-19413-w. BMC Public Health. 2024. PMID: 39080544 Free PMC article.
-
Assessment of public literacy in TB prevention and control in the National 13th Five-Year plan for Tuberculosis Prevention and Control (2016-2020) in China.BMC Health Serv Res. 2025 Jan 9;25(1):50. doi: 10.1186/s12913-024-12155-w. BMC Health Serv Res. 2025. PMID: 39789635 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of the factors influencing the salary level and satisfaction of medical staff in hospitals in less developed areas of Western China based on machine learning algorithms: evidence from Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region.BMC Health Serv Res. 2025 Mar 14;25(1):380. doi: 10.1186/s12913-025-12552-9. BMC Health Serv Res. 2025. PMID: 40087754 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of summer programmes on the outcomes of disadvantaged or 'at risk' young people: A systematic review.Campbell Syst Rev. 2024 Jun 13;20(2):e1406. doi: 10.1002/cl2.1406. eCollection 2024 Jun. Campbell Syst Rev. 2024. PMID: 38873396 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Public sector reforms and their impact on the level of corruption: A systematic review.Campbell Syst Rev. 2021 May 24;17(2):e1173. doi: 10.1002/cl2.1173. eCollection 2021 Jun. Campbell Syst Rev. 2021. PMID: 37131927 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Latent Profile Analysis for Patient Activation in Patients with Essential Hypertension.Patient Prefer Adherence. 2025 Aug 26;19:2635-2645. doi: 10.2147/PPA.S524968. eCollection 2025. Patient Prefer Adherence. 2025. PMID: 40901562 Free PMC article.
References
-
- State council measures to enhance people’s fitness. 2019. https://english.www.gov.cn/policies/latestreleases/201907/15/content_WS5... Available.
-
- Progress and results achieved in the past two years since the implementation of the Healthy China Action [J](in Chinese) Health Economics Research. 2021;08:72.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
