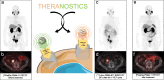
The role of PSMA-based radioligand therapy in hormone-sensitive prostate cancer
- PMID: 39934300
- PMCID: PMC12119734
- DOI: 10.1007/s00259-025-07083-8
The role of PSMA-based radioligand therapy in hormone-sensitive prostate cancer
Abstract
Purpose: Conventional systemic therapies are valuable options in prostate cancer (PCa); however, such treatments can determine adverse events and toxicity. The observed improvement in overall survival, coupled with PSA reduction and a favorable safety profile in the post-taxane castration-resistant PCa (CRPC) setting has prompted the consideration of PSMA-based radioligand therapy (RLT) earlier in the treatment sequence. In this review, we will describe the literature and ongoing clinical trials regarding the use of PSMA-based RLT in hormone-sensitive PCa (HSPC) including the neoadjuvant, de-novo/synchronous metastatic, adjuvant, and early BCR settings.
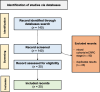
Methods: We performed a systematic literature search on the PubMed/MEDLINE/EMBASE and clinicaltrials.gov databases for studies and protocols assessing the role of PSMA-based RLT in HSPC.
Results: The literature search yielded 140 results. After screening titles and abstracts and applying inclusion and exclusion criteria, we selected 25 papers showing the potentialities of earlier RLT in HSPC, with several ongoing trials.
Conclusion: Early use of PSMA-based RLT holds significant potential in HSPC patients from the neoadjuvant to the BCR setting. In these stages, the lower tumor burden, more frequent exclusive nodal involvement, and higher organ reserve may improve treatment efficacy and allow for treatment combinations while maintaining a less toxic profile.
Keywords: HSPC; PCa; Prostate-specific membrane antigen; RLT; Theranostics.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Consent to publish: Informed consent for the publication of images was received from the participant who appeared in the manuscript. Ethical approval: This is a literature review and therefore no ethical approval is required. Competing interests: The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Figures

References
-
- Rüschoff JH, Ferraro DA, Muehlematter UJ, Laudicella R, Hermanns T, Rodewald AK, et al. What’s behind 68Ga-PSMA-11 uptake in primary prostate cancer PET? Investigation of histopathological parameters and immunohistochemical PSMA expression patterns. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2021;48:4042–53. 10.1007/s00259-021-05501-1. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Laudicella R, Rüschoff JH, Ferraro DA, Brada MD, Hausmann D, Mebert I, et al. Infiltrative growth pattern of prostate cancer is associated with lower uptake on PSMA PET and reduced diffusion restriction on mpMRI. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2022;49:3917–28. 10.1007/s00259-022-05787-9. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bauckneht M, Ciccarese C, Laudicella R, Mosillo C, D’Amico F, Anghelone A, et al. Theranostics revolution in prostate cancer: basics, clinical applications, open issues and future perspectives. Cancer Treat Rev. 2024;124:102698. 10.1016/j.ctrv.2024.102698. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

