Exercise with weight vest plus chicken protein supplementation delayed muscle and bone loss in older female adults
- PMID: 39934626
- PMCID: PMC11811617
- DOI: 10.20463/pan.2024.0028
Exercise with weight vest plus chicken protein supplementation delayed muscle and bone loss in older female adults
Abstract
Purpose: This study examined the effects of moderate-to-heavy exercise training combined with weighted vest and chicken protein supplementation in older adult females.
Methods: Fifty-two female participants, 60-79 yearsold, were randomly divided into three groups: control (non-exercise) (CON), exercise with weighted vest (WV), and exercise with weighted vest and protein supplementation (3 g of protein daily; WVP).A ll participants performed brisk walking and strengthening exercises for 50 min/day, three times/week, for 8 weeks. Muscle mass, bone mineral content, T-score, and physical performance were measured.
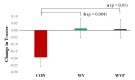
Results: The WVP group demonstrated a substantial increase in thoracic spine bone mineral content (8.4 ± 7.7 g, p = 0.001), and total body lean mass (0.2 ± 1.0 kg) compared with that in the other two groups. The CON and WV groups showed a decrease in thoracic spine bone mineral content (CON= -1.8 ± 1.8, WV= -3.9 ± 0.1 g) and total body lean mass (CON= -0.7 ± 0.9, WV= -0.8 ± 0.9 kg) compared with those in the WVP group. The WVP and WV groups had increased T-score (WVP= 0.01 ± 0.16, WV= 0.02 ± 0.18) when compared with that of the CON group (-0.19 ± 0.12). Both the WV and WVP groups displayed improved physical performance compared with that of the CON group.
Conclusion: Combined exercise with either a weighted vest or protein supplementation proved to be effective in protecting against trunk bone and muscle mass loss, and improving physical fitness in older female adults.
Keywords: bone health; muscle mass; older adults; protein supplementation; resistance exercise; weight vest.
Figures
References
-
- Amarya S, Singh K, Sabharwal M. Ageing process and physiological changes. IntechOpen; 2018.
-
- Marty E, Liu Y, Samuel A, Or O, Lane J. A review of sarcopenia: enhancing awareness of an increasingly prevalent disease. Bone. 2017;105:276–86. - PubMed
-
- Papadopoulou SK, Tsintavis P, Potsaki G, Papandreou D. Differences in the prevalence of sarcopenia in community-dwelling, nursing home and hospitalized individuals. a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Nutr Health Aging. 2020;24:83–90. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources