Exploring the role of perceived social support, and spiritual well-being in predicting the family Caregiving burden among the parents of disabled children
- PMID: 39934710
- PMCID: PMC11816756
- DOI: 10.1186/s12889-025-21654-2
Exploring the role of perceived social support, and spiritual well-being in predicting the family Caregiving burden among the parents of disabled children
Abstract
Background and aim: Caregiver burden encompasses the physical, emotional, financial, and social challenges faced by individuals caring for a sick or disabled person. Spiritual well-being and social support have been identified as protective factors against psychological and physical issues, potentially alleviating caregiver burden. This study aims to explore the relationship between spiritual well-being, perceived social support, and caregiver burden among parents of children with disabilities.
Method: A descriptive-analytical study was conducted with 260 family caregivers, selected through systematic random sampling. Data were collected using a demographic questionnaire, the Novak and Gaug Caregiving Burden Scale, the Paloutzian-Ellison Spiritual Well-being Scale, and the Zimet Social Support Questionnaire. Statistical analysis was performed using IBM SPSS version 22, with significance set at p < 0.05.
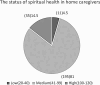
Results: Among the caregivers, 148 (61.4%) reported a high level of caregiving burden, while 81% indicated moderate spiritual well-being and 14.5% reported high spiritual well-being. A significant negative correlation was found between spiritual well-being, social support, and caregiving burden (p < 0.05). Multiple linear regression analysis revealed that spiritual well-being (β = -0.41) and social support (β = -0.33) were the most significant predictors of caregiving burden. Additional significant predictors included social activities, underlying health conditions, age, caregiving duration, insurance coverage, and marital status (p < 0.05).
Conclusion: The high caregiving burden observed in this population, along with the inverse relationship between social support, spiritual well-being, and caregiving burden, underscores the need for strategies to enhance social support and spiritual well-being. These factors may serve as cost-effective, accessible interventions to alleviate caregiving burden.
Keywords: Caregiving burden; Perceived social support; Spiritual well-being.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: The study was approved by the Ethics Committee of Saveh University of Medical Sciences, Ahvaz, Iran (Registration No: IR.SAVEHUMS.REC.1400.010). Written informed consent obtained from participants. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Predictive Role of Perceived Social Support and Psychological Distress on Caregiver Burden in Parents of Children With Cancer.Semin Oncol Nurs. 2025 Jun;41(3):151851. doi: 10.1016/j.soncn.2025.151851. Epub 2025 Apr 5. Semin Oncol Nurs. 2025. PMID: 40187913
-
Caregiver Burden and Spiritual Well-being in Caregivers of Hemodialysis Patients.J Relig Health. 2020 Dec;59(6):3084-3096. doi: 10.1007/s10943-019-00939-y. J Relig Health. 2020. PMID: 31650381
-
The health and well-being of caregivers of children with cerebral palsy.Pediatrics. 2005 Jun;115(6):e626-36. doi: 10.1542/peds.2004-1689. Pediatrics. 2005. PMID: 15930188
-
[Caregiver burden in relatives of persons with schizophrenia: an overview of measure instruments].Encephale. 2003 Mar-Apr;29(2):137-47. Encephale. 2003. PMID: 14567165 Review. French.
-
Parental Experiences of Quality of Life When Caring for Their Children With Intellectual Disability: A Meta-Aggregation Systematic Review.J Appl Res Intellect Disabil. 2025 Jan;38(1):e70005. doi: 10.1111/jar.70005. J Appl Res Intellect Disabil. 2025. PMID: 39763193 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
A Conceptual Model for Strengthening Family Capabilities Through a Process of Care.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2025 Jul 20;22(7):1150. doi: 10.3390/ijerph22071150. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2025. PMID: 40724215 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Savari K, Naseri M, Savari Y. Evaluating the role of perceived stress, social support, and resilience in predicting the quality of life among the parents of disabled children. Int J Disabil Dev Educ. 2023;70(5):644–58.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical