Acute vascular and cardiac effects of lenvatinib in mice
- PMID: 39934897
- PMCID: PMC11816767
- DOI: 10.1186/s40959-025-00307-8
Acute vascular and cardiac effects of lenvatinib in mice
Abstract
Background: Tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) targeting vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) receptor signalling are used in cancer therapy to inhibit angiogenesis. Unfortunately, VEGF inhibitors are known to induce severe hypertension in patients. This study aimed to elucidate the impact of the TKI lenvatinib on blood pressure, arterial stiffness, vascular reactivity, as well as cardiac function in a short-term murine model to shed light on potential contributors to cardiovascular (CV) toxicities associated with VEGF inhibition.
Methods: Male C57BL/6J mice were randomly divided into 2 cohorts, either treated for 4 days with lenvatinib 4 mg/kg/day or 40% hydroxypropyl β-cyclodextrin as control. In an additional study, mice were subjected to a 4-day treatment followed by a 4-day wash-out, with echocardiography and blood pressure measurements performed on day 2 and 7. Subsequently, ex vivo vascular reactivity of thoracic aortic segments was determined.
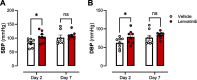
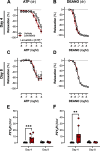
Results: Lenvatinib induced hypertension and arterial stiffness (i.e., increased pulse wave velocity), starting from day 2 of treatment. Further, left ventricular ejection fraction was reduced and the ventricle dilated upon treatment. Lenvatinib induced neither endothelial dysfunction nor impaired vascular smooth muscle cell reactivity to nitric oxide (NO). Interestingly, lenvatinib demonstrated a concentration-dependent increase in ATP-mediated relaxation. In addition, after the 4-day wash-out period, lenvatinib-treated mice did not show complete remission of hypertension. However, arterial stiffness, ATP-mediated relaxation and cardiac adaptation were recovered.
Conclusion: This comprehensive investigation provides valuable insights into the interplay between VEGF inhibition, vascular function and cardiac outcomes, emphasising the need for nuanced understanding and further exploration of the differential effects of lenvatinib on the CV system. Additionally, the study proposes a synergistic formation between VEGF and ATP, indicating an enhanced response via P2Yx receptor signalling.
Keywords: ATP; Cardiovascular toxicity; Hypertension; Lenvatinib; TKIs; VEGFR.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: Use of animals approval of the Ethical Committee for Animal Testing of the University of Antwerp (ethical file 2022–40) conformed with the ARRIVE guidelines, under Directive 2010/63/EU, and with the Belgian Royal Decree of 2013 and the Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals published by the US National Institutes of Health (NIH Publication no.85–23, revised 1996). Welfare of animals was assessed daily by the animal caretakers and the principal researcher based on the Functional Observation Battery scoring system. Criteria for humane euthanasia were as follows: Animals displaying signs of pain based on the scoring table, meeting specific score thresholds, or exhibiting significant weight loss (> 20%). Consent for publication: All authors have read and reviewed the manuscript and agreed to the published version of the manuscript. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures





References
-
- Ferrara N. Adamis AP (2016) Ten years of anti-vascular endothelial growth factor therapy. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2016;156(15):385–403. - PubMed
-
- Ferrara N. Vascular endothelial growth factor: Basic science and clinical progress. Endocr Rev. 2004;25:581–611. - PubMed
-
- Lyon AR, López-Fernánde T, Couch LS, et al. 2022 ESC Guidelines on cardio-oncology developed in collaboration with the European Hematology Association (EHA), the European Society for Therapeutic Radiology and Oncology (ESTRO) and the International Cardio-Oncology Society (IC-OS). Eur Heart J. 2022;43:4229–361. - PubMed
-
- Hussein Z, Mizuo H, Hayato S, Namiki M, Shumaker R. Clinical Pharmacokinetic and Pharmacodynamic Profile of Lenvatinib, an Orally Active, Small-Molecule, Multitargeted Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor. Eur J Drug Metab Pharmacokinet. 2017;42:903–14. - PubMed
Grants and funding
- C/2020/1374/Belgian Foundation against Cancer
- 2021-034/Belgian Foundation against Cancer
- 39984/DOCPRO4 - Antwerp, Belgium
- 49195/Bijzonder Onderzoeksfonds UGent
- 49194/Bijzonder Onderzoeksfonds UAntwerp,Belgium
- I005122N/Research Foundation - Flanders, Belgium
- Funds Pierre Masure, Alphonse & Marie Walckiers, and De Winter-Vermant 2018/King Baudouin Foundation, Belgium
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
