Optimizing therapeutic approaches for HR+/HER2- advanced breast cancer: clinical perspectives on biomarkers and treatment strategies post-CDK4/6 inhibitor progression
- PMID: 39935426
- PMCID: PMC11810462
- DOI: 10.20517/cdr.2024.169
Optimizing therapeutic approaches for HR+/HER2- advanced breast cancer: clinical perspectives on biomarkers and treatment strategies post-CDK4/6 inhibitor progression
Abstract
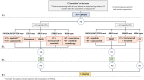
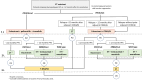
This review offers an expert perspective on biomarkers, CDK4/6 inhibitor efficacy, and therapeutic approaches for managing hormone receptor-positive (HR+), human epidermal growth factor receptor-negative (HER2-) advanced breast cancer (ABC), particularly after CDK4/6 inhibitor progression. Key trials have demonstrated that combining CDK4/6 inhibitors with endocrine therapy (ET) significantly improves progression-free survival (PFS), with median durations ranging from 14.8 to 26.7 months, and overall survival (OS), with median durations reaching up to 53.7 months. Actionable biomarkers, such as PIK3CA and ESR1 mutations, have emerged as pivotal tools to guide second-line treatment decisions, enabling the use of targeted therapies like alpelisib and elacestrant and emphasizing the important role of biomarkers in guiding the selection of therapy. This overview aims to provide clinicians with a practical and up-to-date framework to inform treatment decisions and improve patient care in the context of this challenging disease. Additionally, we review emerging biomarkers and novel treatment strategies to address this difficult clinical landscape.
Keywords: CDK4/6 inhibitors; HR+/HER2-; advanced breast cancer; biomarkers; prognosis.
© The Author(s) 2025.
Conflict of interest statement
Cejalvo Andújar JM declares speaker fees and travel expenses from AstraZeneca, Gilead, Lilly, MSD, Novartis, and Pfizer. Ayala de la Peña F reports consultant or advisor fees from Novartis and Seagen; speaker honoraria from Gilead, Lilly, Novartis, and Pfizer; educational grants and travel expenses from Daichii Sankyo, Gilead, Novartis, Pfizer, and Roche; and research funding from Daichii Sankyo. Margeli Vila M reports consultant or advisor fees from AstraZeneca, Daiichi Sankio, Gilead, Lilly, and Novartis; speaker fees from AstraZeneca, Gilead, Lilly, Novartis, and Pfizer; travel expenses and congress assistance from Gilead, Pfizer, and Roche; and institutional research grants from AstraZeneca, Daiichi Sankio, Eisai, Gilead, NanoString (Translational Research Request), Novartis, Pfizer, and Seagen. Pascual J declares honoraria from AstraZeneca, Novartis, and Pfizer; consultant or advisor fees from AstraZeneca and Novartis; travel and accommodation expenses from AstraZeneca, Gilead Sciences, and Pfizer. Tolosa P declares advisor fees from Adamed, AstraZeneca, Daiichi-Sankyo, Novartis, Roche, and Seagen; speaker honoraria from AstraZeneca, Daiichi-Sankyo, Lilly, MSD, Novartis, Pfizer, and Seagen; travel expenses from AstraZeneca, GSK, Novartis, and Pfizer; and research funding from Seagen. Pages C and Cuenca M are employees at Pfizer Oncology (Spain). Guerrero Zotano A declares consultant or advisor honoraria from AstraZeneca, Exact Science, Novartis, Pierre Fabre, and Stemline; institutional research funding from Pfizer; and speaker fees from AstraZeneca, Daiichi Sankyo, Exact Sciences, MSD, Novartis, Pfizer, Pierre Fabre, and Roche. Some authors may be bound by confidentiality agreements.
Figures
References
-
- Finn RS, Crown JP, Ettl J, et al. Efficacy and safety of palbociclib in combination with letrozole as first-line treatment of ER-positive, HER2-negative, advanced breast cancer: expanded analyses of subgroups from the randomized pivotal trial PALOMA-1/TRIO-18. Breast Cancer Res. 2016;18:67. doi: 10.1186/s13058-016-0721-5. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Rugo HS, Finn RS, Diéras V, et al. Palbociclib plus letrozole as first-line therapy in estrogen receptor-positive/human epidermal growth factor receptor 2-negative advanced breast cancer with extended follow-up. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2019;174:719–29. doi: 10.1007/s10549-018-05125-4. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
