Fusion protein-based COVID-19 vaccines exemplified by a chimeric vaccine based on a single fusion protein (W-PreS-O)
- PMID: 39935478
- PMCID: PMC11811753
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1452814
Fusion protein-based COVID-19 vaccines exemplified by a chimeric vaccine based on a single fusion protein (W-PreS-O)
Abstract
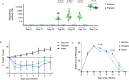
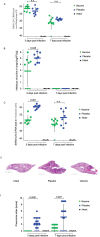
In this article we discuss characteristics of fusion protein-based SARS-CoV-2 vaccines. We focus on recombinant vaccine antigens comprising fusion proteins consisting of combinations of SARS-CoV-2-derived antigens or peptides or combinations of SARS-CoV-2 antigens/peptides with SARS-CoV-2-unrelated proteins/peptides. These fusion proteins are made to increase the immunogenicity of the vaccine antigens and/or to enable special targeting of the immune system. The protein-based vaccine approach is exemplified solely in a proof of concept study by using W-PreS-O, a chimeric vaccine based on a single fusion protein (W-PreS-O), combining RBDs from Wuhan hu-1 wild-type and Omicron BA.1 with the hepatitis B virus (HBV)-derived PreS surface antigen adsorbed to aluminum hydroxide. The W-PreS-O vaccine was evaluated in Syrian hamsters which were immunized three times at three-week intervals with W-PreS-O or with aluminum hydroxide (placebo) before they were infected with Omicron BA.1. Neutralizing antibody (nAB) titers, weight, lung symptoms, and viral loads, as measured using RT-PCR in the upper and lower respiratory tracts, were determined. In addition, infectious virus titers from the lungs were measured using a plaque-forming assay. We found that W-PreS-O-vaccinated hamsters developed robust nABs against Omicron BA.1, showed almost no development of pneumonia, and had significantly reduced infectious virus titers in the lungs. Importantly, the viral loads in the nasal cavities of W-PreS-O-vaccinated hamsters were close to or above the PCR cycle threshold considered to be non-infectious. The data of our proof-of-concept study provides compelling evidence that the W-PreS-O vaccine has protective effect against Omicron BA.1 in a Syrian hamster in vivo infection model and thus support the promising results obtained also for other fusion protein-based SARS-CoV-2 vaccines.
Keywords: COVID-19; SARS-CoV-2; Syrian hamster; fusion protein-based vaccine; infection model; neutralizing antibodies; omicron; vaccine.
Copyright © 2025 Gattinger, Kozlovskaya, Lunin, Gancharova, Sirazova, Apolokhov, Chekina, Gordeychuk, Karaulov, Valenta and Ishmukhametov.
Conflict of interest statement
RV has received research grants from HVD Life-Sciences, Vienna, Austria, WORG Pharmaceuticals, Hangzhou, China and from Viravaxx AG, Vienna, Austria. He serves as consultant for Viravaxx AG. RV and PG are authors on a patent application regarding the vaccine. The authors with Russian affiliation declare that they have prepared the article in their “personal capacity” and/or that they are employed at an academic/research institution where research or education is the primary function of the entity. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Immunogenicity and efficacy of XBB.1.5 rS vaccine against the EG.5.1 variant of SARS-CoV-2 in Syrian hamsters.J Virol. 2024 Oct 22;98(10):e0052824. doi: 10.1128/jvi.00528-24. Epub 2024 Sep 4. J Virol. 2024. PMID: 39230305 Free PMC article.
-
Prototype and BA.5 protein nanoparticle vaccines protect against Omicron BA.5 variant in Syrian hamsters.J Virol. 2024 Mar 19;98(3):e0120623. doi: 10.1128/jvi.01206-23. Epub 2024 Feb 2. J Virol. 2024. PMID: 38305154 Free PMC article.
-
Vaccine Based on Recombinant Fusion Protein Combining Hepatitis B Virus PreS with SARS-CoV-2 Wild-Type- and Omicron-Derived Receptor Binding Domain Strongly Induces Omicron-Neutralizing Antibodies in a Murine Model.Vaccines (Basel). 2024 Feb 23;12(3):229. doi: 10.3390/vaccines12030229. Vaccines (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38543863 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of broad-spectrum protection by novel mRNA vaccines against SARS-CoV-2 variants (Delta, Omicron-BA.5, XBB-EG.5) in the golden hamster model.Virol J. 2025 May 24;22(1):159. doi: 10.1186/s12985-025-02787-7. Virol J. 2025. PMID: 40410742 Free PMC article.
-
A Methyltransferase-Defective Vesicular Stomatitis Virus-Based SARS-CoV-2 Vaccine Candidate Provides Complete Protection against SARS-CoV-2 Infection in Hamsters.J Virol. 2021 Sep 27;95(20):e0059221. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00592-21. Epub 2021 Aug 11. J Virol. 2021. PMID: 34379509 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Moloney Murine Leukemia Virus-like Nanoparticles Pseudo-Typed with SARS-CoV-2 RBD for Vaccination Against COVID-19.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jul 4;26(13):6462. doi: 10.3390/ijms26136462. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40650237 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Menni C, Valdes AM, Polidori L, Antonelli M, Penamakuri S, Nogal A, et al. . Symptom prevalence, duration, and risk of hospital admission in individuals infected with SARS-CoV-2 during periods of omicron and delta variant dominance: a prospective observational study from the ZOE COVID Study. Lancet. (2022) 399:1618–24. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(22)00327-0 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

