Interaction of GPER-1 with the endocrine signaling axis in breast cancer
- PMID: 39936103
- PMCID: PMC11811623
- DOI: 10.3389/fendo.2025.1494411
Interaction of GPER-1 with the endocrine signaling axis in breast cancer
Abstract
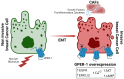
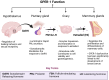
G Protein-Coupled Estrogen Receptor 1 (GPER-1) is a membrane estrogen receptor that has emerged as a key player in breast cancer development and progression. In addition to its direct influence on estrogen signaling, a crucial interaction between GPER-1 and the hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal (HPG) axis has been evidenced. The novel and complex relationship between GPER-1 and HPG implies a hormonal regulation with important homeostatic effects on general organ development and reproductive tissues, but also on the pathophysiology of cancer, especially breast cancer. Recent research points to a great versatility of GPER-1, interacting with classical estrogen receptors and with signaling pathways related to inflammation. Importantly, through its activation by environmental and synthetic estrogens, GPER-1 is associated with hormone therapy resistance in breast cancer. These findings open new perspectives in the understanding of breast tumor development and raise the possibility of future applications in the design of more personalized and effective therapeutic approaches.
Keywords: GPER-1; breast cancer; endocrine resistance; estrogen; hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal axis; personalized medicine.
Copyright © 2025 Molina Calistro, Arancibia, Olivera, Domke and Torres.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
GPER-1/GPR30 a novel estrogen receptor sited in the cell membrane: therapeutic coupling to breast cancer.Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2017 Aug;21(8):755-766. doi: 10.1080/14728222.2017.1350264. Epub 2017 Jul 12. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2017. PMID: 28671018 Review.
-
Possible role of phytoestrogens in breast cancer via GPER-1/GPR30 signaling.Clin Sci (Lond). 2018 Dec 13;132(24):2583-2598. doi: 10.1042/CS20180885. Print 2018 Dec 21. Clin Sci (Lond). 2018. PMID: 30545896 Review.
-
AHR and GPER mediate the stimulatory effects induced by 3-methylcholanthrene in breast cancer cells and cancer-associated fibroblasts (CAFs).J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2019 Aug 1;38(1):335. doi: 10.1186/s13046-019-1337-2. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2019. PMID: 31370872 Free PMC article.
-
Proteolytic Targeting Chimeras with Specificity for Plasma Membrane and Intracellular Estrogen Receptors.Mol Pharm. 2021 Mar 1;18(3):1455-1469. doi: 10.1021/acs.molpharmaceut.1c00018. Epub 2021 Feb 18. Mol Pharm. 2021. PMID: 33600191 Free PMC article.
-
GPER mediates activation of HIF1α/VEGF signaling by estrogens.Cancer Res. 2014 Aug 1;74(15):4053-64. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-13-3590. Epub 2014 Jun 3. Cancer Res. 2014. PMID: 24894716
Cited by
-
Decoding estrogen receptor and GPER biology: structural insights and therapeutic advances in ERα-positive breast cancer.Front Oncol. 2025 Jun 26;15:1513225. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2025.1513225. eCollection 2025. Front Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40641933 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

