The null hypothesis significance test and the dichotomization of the p-value: Errare Humanum Est
- PMID: 39936767
- PMCID: PMC11797584
- DOI: 10.17843/rpmesp.2024.414.14285.
The null hypothesis significance test and the dichotomization of the p-value: Errare Humanum Est
Abstract
Decision-making in healthcare is complex and needs to be based on the best scientific evidence. In this process, information derived from statistical analysis of data is crucial, which can be developed from either frequentist or Bayesian perspectives. When it comes to the frequentist field, the null hypothesis significance test (NHST) and its p-value is one of the most widely used techniques in different disciplines. However, NHST has been subjected to questioning from different academic points of view, which has led to it being considered as one of the causes of the so-called replicability crisis in science. In this review article, we provide a brief historical account of its development, summarize the underlying methods, describe some controversies and limitations, address misuse and misinterpretation, and finally give some scopes and reflections in the context of biomedical research.
La toma de decisiones en salud es compleja y requiere informarse en la mejor evidencia científica. En este proceso, la información generada a partir del análisis estadístico de los datos es crucial, el cual puede desarrollarse desde las perspectivas frecuentista o bayesiana. En la arena frecuentista, la prueba de significancia de la hipótesis nula (PSHN) y el valor p es una de las técnicas de mayor uso en diferentes disciplinas. No obstante, la PSHN desde la academia ha sido sometida a una serie de cuestionamientos desde diversas aristas, lo cual ha conllevado a situarla como una de las causantes de la denominada crisis de replicabilidad en la ciencia. En este artículo de revisión, realizamos un breve recuento histórico sobre su desarrollo, resumimos los métodos subyacentes, describimos algunas controversias y limitaciones, abordamos el mal uso y mala interpretación, para finalmente dar algunos alcances y reflexiones en el contexto de la investigación biomédica.
RESUMEN: La toma de decisiones en salud es compleja y requiere informarse en la mejor evidencia científica. En este proceso, la información generada a partir del análisis estadístico de los datos es crucial, el cual puede desarrollarse desde las perspectivas frecuentista o bayesiana. En la arena frecuentista, la prueba de significancia de la hipótesis nula (PSHN) y el valor p es una de las técnicas de mayor uso en diferentes disciplinas. No obstante, la PSHN desde la academia ha sido sometida a una serie de cuestionamientos desde diversas aristas, lo cual ha conllevado a situarla como una de las causantes de la denominada crisis de replicabilidad en la ciencia. En este artículo de revisión, realizamos un breve recuento histórico sobre su desarrollo, resumimos los métodos subyacentes, describimos algunas controversias y limitaciones, abordamos el mal uso y mala interpretación, para finalmente dar algunos alcances y reflexiones en el contexto de la investigación biomédica.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

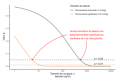
References
-
- Lash TL, VanderWeele TJ, Haneause S, Rothman K. Modern Epidemiology. Wolters Kluwer Health; 2020. pp. 1340–1340.
-
- Hubbard R, Haig BD, Parsa RA. The Limited Role of Formal Statistical Inference in Scientific Inference. Am Stat. 2019;73(sup1):91–98. doi: 10.1080/00031305.2018.1464947. - DOI
-
- Lin H. To Be a Frequentist or Bayesian? Five Positions in a Spectrum. [4 de agosto de 2024];Harv Data Sci Rev. 2024 6(3) doi: 10.1162/99608f92.9a53b923. Internet. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
