Identification of Substituted 4-Aminocinnolines as Broad-Spectrum Antiparasitic Agents
- PMID: 39936822
- PMCID: PMC11915375
- DOI: 10.1021/acsinfecdis.4c00666
Identification of Substituted 4-Aminocinnolines as Broad-Spectrum Antiparasitic Agents
Abstract
Neglected tropical diseases such as Chagas disease, human African trypanosomiasis, leishmaniasis, and schistosomiasis have a significant global health impact in predominantly developing countries, although these diseases are spreading due to increased international travel and population migration. Drug repurposing with a focus on increasing antiparasitic potency and drug-like properties is a cost-effective and efficient route to the development of new therapies. Here we identify compounds that have potent activity against Trypanosoma cruzi and Leishmania donovani, and the latter were progressed into the murine model of infection. Despite the potent in vitro activity, there was no effect on parasitemia, necessitating further work to improve the pharmacokinetic properties of this series. Nonetheless, valuable insights have been obtained into the structure-activity and structure-property relationships of this compound series.
Keywords: Chagas disease; drug repurposing; human African trypanosomiasis; leishmaniasis; neglected tropical diseases; schistosomiasis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures

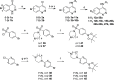
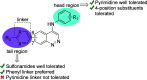


References
-
- World Health Organization . Neglected tropical diseases. https://www.who.int/neglected_diseases/diseases/en/ (accessed October 24, 2024).
-
- Ponte-Sucre A.; Gamarro F.; Dujardin J.-C.; Barrett M. P.; López-Vélez R.; García-Hernández R.; Pountain A. W.; Mwenechanya R.; Papadopoulou B. Drug resistance and treatment failure in leishmaniasis: A 21st century challenge. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2017, 11 (12), e000605210.1371/journal.pntd.0006052. - DOI - PMC - PubMed

