REIMAGINE: A central nervous system basket trial showing safety and efficacy of vafidemstat on aggression in different psychiatric disorders
- PMID: 39936839
- PMCID: PMC12047063
- DOI: 10.1111/pcn.13800
REIMAGINE: A central nervous system basket trial showing safety and efficacy of vafidemstat on aggression in different psychiatric disorders
Abstract
Aim: Vafidemstat is a brain-penetrant, orally bioavailable, small molecule irreversible inhibitor of the histone lysine-specific demethylase KDM1A (also known as LSD1), which corrects memory deficits and behavior alterations including aggression and social interaction deficits in preclinical models.
Methods: Here, we report the results of REIMAGINE, a phase IIa, single-center, open-label, one-arm basket trial that evaluated the safety and efficacy of vafidemstat on aggression in adult patients with borderline personality disorder (BPD), attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), and autistic spectrum disorder (ASD). Participants received 1.2 mg/day of vafidemstat for 8 weeks.
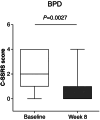
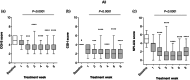
Results: Vafidemstat was shown to be safe and well tolerated, and no drug-related clinically significant adverse events were observed. Furthermore, all neuropsychiatric scales assessed showed notable efficacy signals, whether assessing agitation/aggression (Clinical Global Impression for Severity [CGI-S] and Clinical Global Impression for Improvement [CGI-I] and Neuropsychiatric Inventory [NPI] questionnaire for Agitation-Aggression [NPI-AA]), overall patient functioning (total NPI), or disease-specific features (Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder Rating Scale [ADHD-RS] and Borderline Personality Disorder Checklist [BPDCL]). Statistically significant improvements were observed in the aggregated data (all participants) and for each of the three disease groups independently. Changes were evident within the first 2 weeks of treatment.
Conclusion: In summary, the REIMAGINE study supports that vafidemstat is safe, well tolerated, and causes a significant and consistent reduction in agitation/aggression and nonaggression features in BPD, ADHD, and ASD. These data support continuing the development of vafidemstat as a new treatment option for these psychiatric disorders.
Keywords: aggression; attention‐deficit/hyperactivity disorder; autistic spectrum disorder; borderline personality disorder; vafidemstat.
© 2025 The Author(s). Psychiatry and Clinical Neurosciences published by John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd on behalf of Japanese Society of Psychiatry and Neurology.
Figures




References
-
- Redig AJ, Jänne PA. Basket trials and the evolution of clinical trial design in an era of genomic medicine. J. Clin. Oncol. 2015; 33: 975–977. - PubMed
-
- Hodges A, Strand AD, Aragaki AK et al. Regional and cellular gene expression changes in human Huntington's disease brain. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2006; 15: 965–977. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

