Treatments and Outcomes of Newly Diagnosed CD5-Positive Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma: A Multi-Institutional Observational Study
- PMID: 39937961
- PMCID: PMC11819764
- DOI: 10.1002/hon.70047
Treatments and Outcomes of Newly Diagnosed CD5-Positive Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma: A Multi-Institutional Observational Study
Abstract
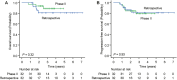
CD5-positive diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (CD5+ DLBCL) is characterized by a poor prognosis and frequent central nervous system (CNS) relapse. Sandwich therapy comprising dose-adjusted (DA)-EPOCH-R (etoposide, prednisolone, vincristine, cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, and rituximab) and high-dose methotrexate (HD-MTX) (DA-EPOCH-R/HD-MTX) showed excellent efficacy and manageable safety in a phase II study of patients diagnosed with stage II-IV CD5+ DLBCL. To validate the results of that study and elucidate the current state of treatment for CD5+ DLBCL, we retrospectively analyzed the outcomes of patients with CD5+ DLBCL diagnosed between 2016 and 2021 who received anthracycline-containing chemotherapy with rituximab. Among the 346 patients evaluated, 62 (18%) received DA-EPOCH-R/HD-MTX. The median follow-up time was 43 months. In 55 patients with stage II-IV disease treated with DA-EPOCH-R/HD-MTX, the 2-year overall survival (OS), progression-free survival, and cumulative incidence of CNS relapse were 87% (95% CI, 73%-94%), 76% (95% CI, 61%-86%), and 7.3% (95% CI, 2.4%-16%), respectively. There were no treatment-related deaths. Febrile neutropenia occurred in 18 (33%) patients. Multivariate analysis of the 346 patients identified elevated serum lactate dehydrogenase levels, multiple extranodal involvement, no intrathecal MTX (IT-MTX), and no DA-EPOCH-R/HD-MTX as independent risk factors for OS. Only one CNS relapse event was observed in 28 patients who received both HD-MTX and IT-MTX. Our study provides real-world data on the treatments and outcomes of a large number of patients. The favorable survival and manageable toxicity of DA-EPOCH-R/HD-MTX have been validated in clinical settings. The use of HD-MTX and IT-MTX might be effective for preventing CNS relapse in patients with CD5+ DLBCL.
Keywords: CD5 antigen; central nervous system neoplasms; diffuse large B‐cell lymphoma; methotrexate; retrospective study.
© 2025 The Author(s). Hematological Oncology published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
Y.N. reports grants from AstraZeneca, Genmab, Incyte, AbbVie, Eisai, Takeda, Otsuka, Chugai, Asahi Kasei, Sumitomo Pharma and Kyowa Kirin and honoraria from Chugai and Nippon Shinyaku. K.M. reports grants from Eisai, Takeda, Nippon Shinyaku, Otsuka, Chugai, Asahi Kasei, Sumitomo Pharma, Kyowa Kirin and Zenyaku and honoraria from Chugai, SymBio, Janssen, Eisai, Nippon Shinyaku, AstraZeneca, Bristol Myers Squibb, Meiji Seika, AbbVie, Novartis, Incyte, Asahi Kasei, Ono, Kyowa Kirin and Genmab. D.M. reports grants from Amgen, Celgene, Kyowa Kirin, Novartis, Chugai, Ono, Takeda, Janssen, Sanofi, Otsuka, Bristol Myers Squibb, Astellas, Eisai, AbbVie, Taiho, MSD and Pfizer; consulting fees from Pfizer and honoraria from Ono, Celgene, Nippon Shinyaku, Janssen, Mundipharma, Eisai, Chugai, Kyowa Kirin, MSD, Zenyaku, Sanofi, SymBio, Takeda, AbbVie, Bristol Myers Squibb and AstraZeneca. H.T. reports honoraria from AstraZeneca, Bristol Meyers Squibb, Chugai, Janssen, Kyowa Kirin, Meiji Seika, Nippon Shinyaku, Mundipharma, Takeda, SymBio, Ono, Eisai and Sanofi. K.S. reports grants from AbbVie, Incyte, GSK, Sanofi, Novartis, Pfizer, Bristol Myers Squibb, Janssen, BeiGene, Kyowa Kirin, Ono, Otsuka and Chugai and honoraria from Bristol Myers Squibb, Sanofi and Janssen. E.N. reports honoraria from Chugai, Sumitomo Pharma, Kyowa Kirin, Janssen, Mundipharma, AstraZeneca, Ono, Takeda, Meiji Seika, Novartis, Bristol Myers Squibb and Nippon Kayaku. N. Takayama reports grants from Chugai, Takeda, Kyowa Kirin and Asahi Kasei and honoraria from AbbVie, Novartis, Janssen, Ono, Pfizer, Bristol Myers Squibb, Sanofi, Otsuka, Meiji Seika, Chugai, Takeda, Kyowa Kirin and Asahi Kasei. S.M. reports honoraria from Chugai, SymBio and Takeda. M. Yoshida reports honoraria from Takeda, Novartis and Astellas. M.N. reports grants from SymBio, Chugai and Kyowa Kirin and honoraria from Chugai, Kyowa Kirin, Eisai, Takeda, Nippon Shinyaku, Janssen, Sumitomo Pharma, AstraZeneca, AbbVie, SymBio, Bristol Myers Squibb, Genmab, Ono and Otsuka. I.T. reports grants from Asahi Kasei, Chugai, Eisai, Kyowa Kirin, Nippon Shinyaku, Otsuka, Sumitomo Pharma and Takeda and honoraria from AbbVie, Alexion, Asahi Kasei, Astellas, AstraZeneca, Bristol Myers Squibb, Chugai, CSL Behring, Eisai, Janssen, Kyowa Kirin, Nippon Shinyaku, Novartis, Novo Nordisk, Otsuka, Pfizer, Sanofi, Sumitomo Pharma, SymBio and Takeda. N.A. reports honoraria from Takeda and Eisai. K.I. reports grants from Chugai, Bristol Myers Squibb, Incyte, Genmab, LOXO Oncology, Daiichi Sankyo, Beigene, AbbVie, AstraZeneca, Regeneron, Yakult, Otsuka, Novartis, Pfizer, MSD, Bayer, Kyowa Kirin, Eisai, Janssen, Ono, Gilead and Amgen; consulting fees from AstraZeneca, Ono, Mitsubishi Tanabe, Eisai, Chugai, Bristol Myers Squibb, AbbVie, Takeda, Zenyaku, Genmab, Kyowa Kirin, MSD, Carna Biosciences, Novartis, Yakult, Nihon Shinyaku, Novartis and Beigene and honoraria from AstraZeneca, Ono, Eisai, Chugai, Janssen, Symbio, Bristol Myers Squibb, Daiichi Sankyo, Otsuka, AbbVie, Takeda, Eli Lilly, Genmab, Kyowa Kirin, MSD, Astellas, Pfizer, Meiji Seika, Novartis, Nihon Kayaku and Gilead. K.K. reports grants from AbbVie, MSD, Bristol Myers Squibb, Chugai, Daiichi Sankyo, Eisai, Janssen, Kyowa Kirin, Novartis and Ono; consulting fees from AbbVie, AstraZeneca, Chugai, Daiichi Sankyo, Eisai, Janssen and Novartis; and honoraria from Bristol Myers Squibb, Chugai, Dainippon Sumitomo, Janssen, Kyowa Kirin, MSD, Ono and Novartis. R.S. reports grants from Chugai, Kyowa Kirin, Shionogi, Taiho, Eisai and Ohtsuka and honoraria from Chugai, Kyowa Kirin, AbbVie, Bristol Meyers Squib, Eisai, Ohtsuka, MSD, Janssen, Takeda, Meiji Seika, Novartis and AstraZeneca. M. Yamaguchi reports grants from AstraZeneca, Chugai, Genmab, Incyte and AbbVie; consulting fees from Genmab, BeiGene and Nihon Servier; and honoraria from Chugai, Kyowa Kirin, AbbVie, Bristol Myers Squibb, Janssen, Meiji Seika, MSD, Nippon Shinyaku, SymBio, Takeda and Eisai.
Figures


References
-
- Swerdlow S. H., Campo E., Harris N. L., et al., WHO Classification of Tumours of Haematopoietic and Lymphoid Tissues. Revised 4th ed. (Lyon: IARC Press, 2017).
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

