High Prevalence of Ceftriaxone-Resistant Neisseria gonorrhoeae in Hanoi, Vietnam, 2023-2024
- PMID: 39938052
- PMCID: PMC12308657
- DOI: 10.1093/infdis/jiaf071
High Prevalence of Ceftriaxone-Resistant Neisseria gonorrhoeae in Hanoi, Vietnam, 2023-2024
Abstract
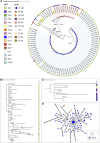
Ceftriaxone resistance in Neisseria gonorrhoeae is an escalating global health concern, threatening the efficacy of empiric treatment. In the Asia-Pacific region, a rapid surge in ceftriaxone resistance has been observed, primarily associated with the penA-60.001 allele. This study, conducted in Hanoi, Vietnam between 2023 and 2024, analyzed 352 N. gonorrhoeae isolates and found a 27% prevalence of ceftriaxone resistance. Whole-genome sequencing identified that resistance was predominantly driven by the mosaic penA-237.001 allele, with a smaller contribution from penA-60.001. The high prevalence of resistance and the emergence of new alleles underscore the urgent threat to ceftriaxone as an empiric treatment option.
Keywords: Asia, Southeastern; antimicrobial resistance; ceftriaxone; gonorrhea; whole-genome sequencing.
© The Author(s) 2025. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Infectious Diseases Society of America.
Conflict of interest statement
Potential conflicts of interest : All authors declare no conflicts of interest. All authors have submitted the ICMJE Form for Disclosure of Potential Conflicts of Interest. Conflicts that the editors consider relevant to the content of the manuscript have been disclosed. Presented in part: 25th International Union Against Sexually Transmitted Infections World Congress, September 2024, Sydney, Australia.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

