Radiomic analysis of patient and interorgan heterogeneity in response to immunotherapies and BRAF-targeted therapy in metastatic melanoma
- PMID: 39939139
- PMCID: PMC11822426
- DOI: 10.1136/jitc-2024-009568
Radiomic analysis of patient and interorgan heterogeneity in response to immunotherapies and BRAF-targeted therapy in metastatic melanoma
Abstract
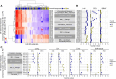
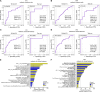
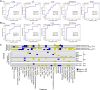
Variability in treatment response may be attributable to organ-level heterogeneity in tumor lesions. Radiomic analysis of medical images can elucidate non-invasive biomarkers of clinical outcome. Organ-specific radiomic comparison across immunotherapies and targeted therapies has not been previously reported. We queried the UPMC Hillman Cancer Center registry for patients with metastatic melanoma (MEL) treated with immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICI) (anti-programmed cell death protein-1 (PD-1)/cytotoxic T-lymphocyte associated protein 4 (CTLA-4) (ipilimumab+nivolumab; I+N) or anti-PD-1 monotherapy) or BRAF-targeted therapy. The best overall response was measured using Response Evaluation Criteria in Solid Tumors V.1.1. Lesions were segmented into discrete volume-of-interest with 400 radiomics features extracted. Overall and organ-specific machine-learning models were constructed to predict disease control (DC) versus progressive disease (PD) using XGBoost. 291 patients with MEL were identified, including 242 ICI (91 I+N, 151 PD-1) and 49 BRAF. 667 metastases were analyzed, including 541 ICI (236 I+N, 305 PD-1) and 126 BRAF. Across cohorts, baseline demographics included 39-47% women, 24%-29% M1C, 24-46% M1D, and 61-80% with elevated lactate dehydrogenase. Among ICI patients experiencing DC, the organs with the greatest reduction were liver (-66%±8%; mean±SEM) and lung (-63%±5%). For patients with multiple same-organ target lesions, the highest interlesion heterogeneity was observed in brain among patients who received ICI while no intraorgan heterogeneity was observed in BRAF. 221 ICI patients were included for radiomic modeling, consisting of 86 I+N and 135 PD-1. Models consisting of optimized radiomic signatures classified DC/PD across I+N (area under curve (AUC)=0.85) and PD-1 (0.71) and within individual organ sites (AUC=0.72~0.94). Integration of clinical variables improved the models' performance. Comparison of models between treatments and across organ sites suggested mostly non-overlapping DC or PD features. Skewness, kurtosis, and informational measure of correlation (IMC) were among the radiomic features shared between overall response models. Kurtosis and IMC were also used by multiple organ-site models. In conclusion, differential organ-specific response was observed across BRAF and ICI with within organ heterogeneity observed for ICI but not for BRAF. Radiomic features of organ-specific response demonstrated little overlap. Integrating clinical factors with radiomics improves the prediction of disease course outcome and prediction of tumor heterogeneity.
Keywords: Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor; Immunotherapy; Skin Cancer.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2025. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ Group.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: RB declares PCT/US15/612657 (Cancer Immunotherapy), PCT/US18/36052 (Microbiome Biomarkers for Anti-PD-1/PD-L1 Responsiveness: Diagnostic, Prognostic and Therapeutic Uses Thereof), PCT/US63/055227 (Methods and Compositions for Treating Autoimmune and Allergic Disorders); JJL declares DSMB: AbbVie, Immutep; Scientific Advisory Board: (no stock) 7 Hills, Fstar, Inzen, RefleXion, Xilio (stock) Actym, Alphamab Oncology, Arch Oncology, Kanaph, Mavu, Onc.AI, Pyxis, Tempest; Consultancy with compensation: AbbVie, Alnylam, Avillion, Bayer, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Checkmate, Codiak, Crown, Day One, Eisai, EMD Serono, Flame, Genentech, Gilead, HotSpot, Kadmon, KSQ, Janssen, Ikena, Immunocore, Incyte, Macrogenics, Merck, Mersana, Nektar, Novartis, Pfizer, Regeneron, Ribon, Rubius, Silicon, Synlogic, Synthekine, TRex, Werewolf, Xencor; Research Support: (all to institution for clinical trials unless noted) AbbVie, Agios (IIT), Astellas, AstraZeneca, Bristol-Myers Squibb (IIT & industry), Corvus, Day One, EMD Serono, Fstar, Genmab, Ikena, Immatics, Incyte, Kadmon, KAHR, Macrogenics, Merck, Moderna, Nektar, Next Cure, Numab, Pfizer (IIT & industry) Replimmune, Rubius, Scholar Rock, Synlogic, Takeda, Trishula, Tizona, Xencor; Patents: (both provisional) Serial #15/612,657 (Cancer Immunotherapy), PCT/US18/36052 (Microbiome Biomarkers for Anti-PD-1/PD-L1 Responsiveness: Diagnostic, Prognostic and Therapeutic Uses Thereof). P.C.L. declares equity interest in Amgen. D.D. declares grants/research support (NIH/NCI and Checkmate Pharmaceuticals) and consulting (Checkmate Pharmaceuticals) during the conduct of the study. D.D. also reports grants/research support (Arcus, CellSight Technologies, Immunocore, Merck Sharp & Dohme, Tesaro/GSK), consulting [Clinical Care Options (CCO), Finch Therapeutics, Gerson Lehrman Group (GLG), Medical Learning Group (MLG), Xilio Therapeutics], speakers' bureau (Castle Biosciences) and pending provisional patents related to gut microbial signatures of response and toxicity to immune checkpoint blockade (US Patent 63/124,231 and US Patent 63/208,719) outside the submitted work. J.M.K. declares grants/research support (Bristol-Myers Squibb, Amgen Inc.) and consulting (Bristol-Myers Squibb, Checkmate Pharmaceuticals, Novartis, Amgen Inc., Checkmate, Castle Biosciences, Inc., Immunocore LLC, Iovance, Novartis.) outside the submitted work. H.M.Z. declares grants/research support (NIH/NCI and Checkmate Pharmaceuticals) and consulting (Checkmate Pharmaceuticals) during the conduct of the study, grants/research support (NIH/NCI, Bristol-Myers Squibb and GlaxoSmithKline), personal fees (GlaxoSmithKline and Vedanta) and pending provisional patents related to gut microbial signatures of response and toxicity to immune checkpoint blockade (US Patent 63/124,231 and US Patent 63/208,719) outside the submitted work. Y.G.N. declares consulting/advisory board (Immunocore, replimune, BMS, Pfizer, Novartis, Merck, Mallinkrodt, Intervenn bio), research to institution (BMS, Pfizer, Merck, replimune), and speaker (Immunocore, Pfizer). Correspondence and requests for materials should be addressed to R.B. (baor@upmc.edu) and J.J.L. (lukejj@upmc.edu). The remaining authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Update of
-
Radiomic analysis of patient and inter-organ heterogeneity in response to immunotherapies and BRAF targeted therapy in metastatic melanoma.medRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Apr 27:2024.04.26.24306411. doi: 10.1101/2024.04.26.24306411. medRxiv. 2024. Update in: J Immunother Cancer. 2025 Feb 12;13(2):e009568. doi: 10.1136/jitc-2024-009568. PMID: 38712112 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
