Negative refraction of light in an atomic medium
- PMID: 39939587
- PMCID: PMC11822078
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-025-56250-w
Negative refraction of light in an atomic medium
Abstract
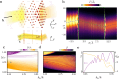
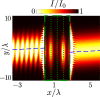
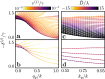
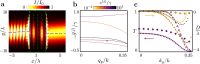
The quest to manipulate light propagation in ways not possible with natural media has driven the development of artificially structured metamaterials. One of the most striking effects is negative refraction, where the light beam deflects away from the boundary normal. However, due to material characteristics, the applications of this phenomenon, such as lensing that surpasses the diffraction limit, have been constrained. Here, we demonstrate negative refraction of light in an atomic medium without the use of artificial metamaterials, employing essentially exact simulations of light propagation. High transmission negative refraction is achieved in atomic arrays for different level structures and lattice constants, within the scope of currently realised experimental systems. We introduce an intuitive description of negative refraction based on collective excitation bands, whose transverse group velocities are antiparallel to the excitation quasi-momenta. We also illustrate how this phenomenon is robust to lattice imperfections and can be significantly enhanced through subradiance.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

