Selected Plant Extracts Regulating the Inflammatory Immune Response and Oxidative Stress: Focus on Quercus robur
- PMID: 39940368
- PMCID: PMC11820342
- DOI: 10.3390/nu17030510
Selected Plant Extracts Regulating the Inflammatory Immune Response and Oxidative Stress: Focus on Quercus robur
Abstract
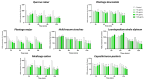
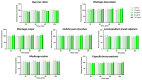
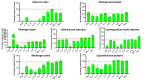
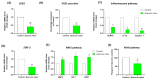
Background/Objectives: Inflammation is a vital response of the immune system, frequently linked to the development and progression of numerous chronic and autoimmune diseases. Targeting inflammation represents an attractive strategy to prevent and treat these pathologies. In this context, many pathways, including pro-inflammatory cytokines secretion, NFκB activation, reactive oxygen species (ROS) production, inflammasome activation and arachidonic acid metabolism could be highlighted and addressed. Several plant materials have traditionally been used as effective and non-harmful anti-inflammatory agents. However, well-established scientific evidence is lacking, and their mechanisms of action remain unclear. The current article compares the effects of seven plant extracts, including Quercus robur L. (Oak), Plantago lanceolata L. (narrowleaf plantain), Plantago major L. (broadleaf plantain), Helichrysum stoechas L. (immortelle or helichrysum), Leontopodium nivale alpinum Cass. (edelweiss), Medicago sativa L. (alfafa) and Capsella bursa-pastoris Moench (shepherd's purse) on different inflammatory pathways. Results: All of the plant extracts significantly affected ROS production, but their action on cytokine production was more variable. As the Quercus robur extract showed the highest efficacy in our models, it was subsequently assessed on several inflammatory signaling pathways. Quercus robur significantly decreased the secretion of IFNγ, IL-17a, IL-12, IL-2, IL-1β and IL-23 in stimulated human leucocytes, and the expression of TNFα, IL-6, IL-8, IL-1β and CXCL10 in M1-like macrophages. Additionally, a significant reduction in PGE2 secretion, COX2, NLRP3, caspase1 and STAT3 expression and NFκB p65 phosphorylation was observed. Conclusions: Our results clearly indicate that Quercus robur has a potent anti-inflammatory effect, making it a promising candidate for both the treatment and prevention of inflammation and related diseases, thereby promoting overall well-being.
Keywords: Quercus robur; antioxidant; inflammation; macrophages; plant extracts.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare the following financial interests/personal relationships which may be considered as potential competing interests: A. Chervet, A. Rousset and J.-Y. Berthon were employed by the company Greentech. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Harvanová G., Duranková S., Bernasovská J. The Role of Cytokines and Chemokines in the Inflammatory Response. Alergol. Pol. Pol. J. Allergol. 2023;10:210–219. doi: 10.5114/pja.2023.131708. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

