The Role of Myokines in Liver Diseases
- PMID: 39940810
- PMCID: PMC11817747
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms26031043
The Role of Myokines in Liver Diseases
Abstract
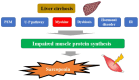
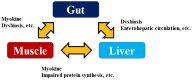
Myokine is a general term for hormones, peptides, and other substances secreted by skeletal muscle. Myokine has attracted much attention in recent years as a key substance for understanding the mechanism of "exercise and health". Skeletal muscle accounts for about 40% of the total human weight and is now recognized as an endocrine organ that produces myokines, which have physiological activity. Representative myokines include IL-6, myostatin, irisin, brain-derived neurotropic factor, fibroblast growth factor-21, and decorin. On the other hand, sarcopenia, defined by quantitative and qualitative loss of skeletal muscle, is a condition that has received much attention in recent years because of its close correlation with prognosis. In patients with chronic liver disease (CLD), sarcopenia is a common complication. Mechanisms underlying sarcopenia in CLD patients have been reported to involve protein-energy malnutrition, which is characteristic of patients with cirrhosis, signaling involved in protein synthesis and degradation, myokines such as myostatin and decorin, the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway, sex hormones such as testosterone, dysbiosis, and insulin resistance, etc., in addition to aging. Each of these pathological conditions is thought to be intricately related to each other, leading to sarcopenia. This review will summarize the relationship between CLD and myokines.
Keywords: IL-6; liver; muscle–gut–liver axis; myokine; myostatin; sarcopenia.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical