Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy for the Treatment of Bone-Related Diseases
- PMID: 39940834
- PMCID: PMC11817436
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms26031067
Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy for the Treatment of Bone-Related Diseases
Abstract
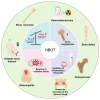
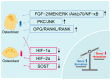
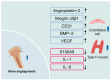
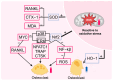
Hyperbaric oxygen therapy (HBOT) is a therapeutic modality that enhances tissue oxygenation by delivering 100% oxygen at pressures greater than 1 absolute atmosphere. In recent years, HBOT has shown considerable potential in the treatment of bone diseases. While excess oxygen was once thought to induce oxidative stress, recent studies indicate that when administered within safe limits, HBOT can notably promote bone healing and repair. Extensive basic research has demonstrated that HBOT can stimulate the proliferation and differentiation of osteoblasts and encourage bone angiogenesis. Furthermore, HBOT has been shown to exert a beneficial influence on bone metabolism by modulating the inflammatory response and redox status. These mechanisms are closely related to core issues of bone biology. Specifically, in the context of fracture healing, bone defect repair, and conditions such as osteoporosis, HBOT targets the key bone signaling pathways involved in bone health, thereby exerting a therapeutic effect. Several clinical studies have demonstrated the efficacy of HBOT in improving bone health. However, the optimal HBOT regimen for treating various bone diseases still requires further definition to expand the indications for its clinical application. This paper outlines the mechanisms of HBOT, focusing on its antioxidant stress, promotion of bone vascularization, and anti-inflammatory properties. The paper also describes the application of HBOT in orthopedic diseases, thereby providing a scientific basis for the development of precise and personalized HBOT treatment regimens in clinical orthopedics.
Keywords: bone; bone formation; bone resorption; hyperbaric oxygen therapy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Poorly designed research does not help clarify the role of hyperbaric oxygen in the treatment of chronic diabetic foot ulcers.Diving Hyperb Med. 2016 Sep;46(3):133-134. Diving Hyperb Med. 2016. PMID: 27723012
-
Hyperbaric oxygen therapy for healthy aging: From mechanisms to therapeutics.Redox Biol. 2022 Jul;53:102352. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2022.102352. Epub 2022 May 27. Redox Biol. 2022. PMID: 35649312 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy: A New Treatment for Chronic Pain?Pain Pract. 2016 Jun;16(5):620-8. doi: 10.1111/papr.12312. Epub 2015 May 19. Pain Pract. 2016. PMID: 25988526 Review.
-
Hyperbaric Oxygen Exposure Attenuates Circulating Stress Biomarkers: A Pilot Interventional Study.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020 Oct 27;17(21):7853. doi: 10.3390/ijerph17217853. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020. PMID: 33120884 Free PMC article.
-
Hyperbaric oxygen therapy improves age induced bone dyshomeostasis in non-obese and obese conditions.Life Sci. 2022 Apr 15;295:120406. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2022.120406. Epub 2022 Feb 16. Life Sci. 2022. PMID: 35182555
Cited by
-
Early Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy Promotes Recovery of Blunt Liver Injury in Rats via Inhibiting Inflammatory Response and Oxidative Stress.Int J Med Sci. 2025 Apr 13;22(9):2174-2185. doi: 10.7150/ijms.109842. eCollection 2025. Int J Med Sci. 2025. PMID: 40303491 Free PMC article.
-
The Impact of Recreational Diving to a Depth of 40 m on Selected Intracellular DAMPs.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Mar 27;26(7):3061. doi: 10.3390/ijms26073061. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40243713 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

